The proline-rich peptide Bac7(1-35) reduces mortality from Salmonella typhimurium in a mouse model of infection
- PMID: 20573188
- PMCID: PMC2896951
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-178
The proline-rich peptide Bac7(1-35) reduces mortality from Salmonella typhimurium in a mouse model of infection
Abstract
Background: Bac7 is a proline-rich peptide with a potent in vitro antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Here we investigated its activity in biological fluids and in vivo using a mouse model of S. typhimurium infection.
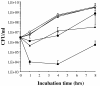
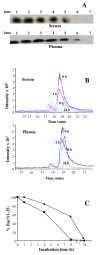
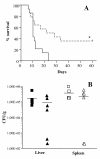
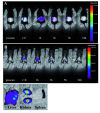
Results: The efficacy of the active 1-35 fragment of Bac7 was assayed in serum and plasma, and its stability in biological fluids analyzed by Western blot and mass spectrometry. The ability of the peptide to protect mice against Salmonella was assayed in a typhoid fever model of infection by determination of survival rates and bacterial load in liver and spleen of infected animals. In addition, the peptide's biodistribution was evaluated by using time-domain optical imaging. Bac7(1-35) retained a substantial in vivo activity showing a very low toxicity. The peptide increased significantly the number of survivors and the mean survival times of treated mice reducing the bacterial load in their organs despite its rapid clearance.
Conclusions: Our results provide a first indication for a potential development of Bac7-based drugs in the treatment of salmonellosis and, eventually, other Gram-negative infections. The in vivo activity for this peptide might be substantially enhanced by decreasing its excretion rate or modifying the treatment schedule.
Figures
References
-
- Zanetti M. The role of cathelicidins in the innate host defenses of mammals. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2005;7(2):179–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

