hand2 and Dlx genes specify dorsal, intermediate and ventral domains within zebrafish pharyngeal arches
- PMID: 20573696
- PMCID: PMC2927700
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.049700
hand2 and Dlx genes specify dorsal, intermediate and ventral domains within zebrafish pharyngeal arches
Abstract
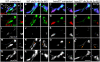
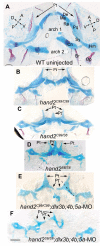
The ventrally expressed secreted polypeptide endothelin1 (Edn1) patterns the skeleton derived from the first two pharyngeal arches into dorsal, intermediate and ventral domains. Edn1 activates expression of many genes, including hand2 and Dlx genes. We wanted to know how hand2/Dlx genes might generate distinct domain identities. Here, we show that differential expression of hand2 and Dlx genes delineates domain boundaries before and during cartilage morphogenesis. Knockdown of the broadly expressed genes dlx1a and dlx2a results in both dorsal and intermediate defects, whereas knockdown of three intermediate-domain restricted genes dlx3b, dlx4b and dlx5a results in intermediate-domain-specific defects. The ventrally expressed gene hand2 patterns ventral identity, in part by repressing dlx3b/4b/5a. The jaw joint is an intermediate-domain structure that expresses nkx3.2 and a more general joint marker, trps1. The jaw joint expression of trps1 and nkx3.2 requires dlx3b/4b/5a function, and expands in hand2 mutants. Both hand2 and dlx3b/4b/5a repress dorsal patterning markers. Collectively, our work indicates that the expression and function of hand2 and Dlx genes specify major patterning domains along the dorsoventral axis of zebrafish pharyngeal arches.
Figures







References
-
- Angelo S., Lohr J., Lee K. H., Ticho B. S., Breitbart R. E., Hill S., Yost H. J., Srivastava D. (2000). Conservation of sequence and expression of Xenopus and zebrafish dHAND during cardiac, branchial arch and lateral mesoderm development. Mech. Dev. 95, 231-237 - PubMed
-
- Beverdam A., Merlo G. R., Paleari L., Mantero S., Genova F., Barbieri O., Janvier P., Levi G. (2002). Jaw transformation with gain of symmetry after Dlx5/Dlx6 inactivation: mirror of the past? Genesis 34, 221-227 - PubMed
-
- Crump J. G., Swartz M. E., Eberhart J. K., Kimmel C. B. (2006). Moz-dependent Hox expression controls segment-specific fate maps of skeletal precursors in the face. Development 133, 2661-2669 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

