A stimulatory role for the La-related protein 4B in translation
- PMID: 20573744
- PMCID: PMC2905749
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2146910
A stimulatory role for the La-related protein 4B in translation
Abstract
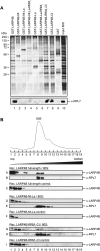
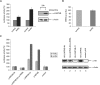
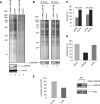
La-related proteins (LARPs) belong to an evolutionarily conserved family of factors with predicted roles in RNA metabolism. Here, we have analyzed the cellular interactions and function of LARP4B, a thus far uncharacterized member of the LARP family. We show that LARP4B is a cytosolic protein that accumulates upon arsenite treatment in cellular stress granules. Biochemical experiments further uncovered an interaction of LARP4B with the cytosolic poly(A) binding protein 1 (PABPC1) and the receptor for activated C Kinase (RACK1), a component of the 40S ribosomal subunit. Under physiological conditions, LARP4B co-sedimented with polysomes in cellular extracts, suggesting a role in translation. In agreement with this notion, overexpression of LARP4B stimulated protein synthesis, whereas knockdown of the factor by RNA interference impaired translation of a large number of cellular mRNAs. In sum, we identified LARP4B as a stimulatory factor of translation. We speculate that LARP4B exerts its function by bridging mRNA factors of the 3' end with initiating ribosomes.
Figures
References
-
- Aigner S, Postberg J, Lipps HJ, Cech TR 2003. The Euplotes La motif protein p43 has properties of a telomerase-specific subunit. Biochemistry 42: 5736–5747 - PubMed
-
- Alfano C, Sanfelice D, Babon J, Kelly G, Jacks A, Curry S, Conte MR 2004. Structural analysis of cooperative RNA binding by the La motif and central RRM domain of human La protein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 323–329 - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N 2008. Stress granules: The Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci 33: 141–150 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
