Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by different organochalchogens is mediated by thiol oxidation and is not dependent of the classical mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening
- PMID: 20573786
- PMCID: PMC2923288
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq185
Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by different organochalchogens is mediated by thiol oxidation and is not dependent of the classical mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening
Abstract
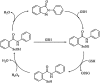
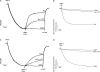
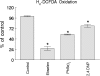
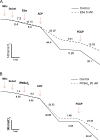
Ebselen (Ebs) and diphenyl diselenide [(PhSe)(2)] readily oxidize thiol groups. Here we studied mitochondrial swelling changes in mitochondrial potential (Deltapsim), NAD(P)H oxidation, reactive oxygen species production, protein aggregate formation, and oxygen consumption as ending points of their in vitro toxicity. Specifically, we tested the hypothesis that organochalchogens toxicity could be associated with mitochondrial dysfunction via oxidation of vicinal thiol groups that are known to be involved in the regulation of mitochondrial permeability (Petronilli et al. J. Biol. Chem., 269; 16638; 1994). Furthermore, we investigated the possible mechanism(s) by which these organochalchogens could disrupt liver mitochondrial function. Ebs and (PhSe)(2) caused mitochondrial depolarization and swelling in a concentration-dependent manner. Furthermore, both organochalchogens caused rapid oxidation of the mitochondrial pyridine nucleotides (NAD(P)H) pool, likely reflecting the consequence and not the cause of increased mitochondrial permeability (Costantini, P., Chernyak, B. V., Petronilli, V., and Bernardi, P. (1996). Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) by pyridine nucleotides and dithiol oxidation at two separate sites. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6746-6751). The organochalchogens-induced mitochondrial dysfunction was prevented by the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT). Ebs- and (PhSe)(2)-induced mitochondrial depolarization and swelling were unchanged by ruthenium red (4microM), butylated hydroxytoluene (2.5microM), or cyclosporine A (1microM). N-ethylmaleimide enhanced the organochalchogens-induced mitochondrial depolarization, without affecting the magnitude of the swelling response. In contrast, iodoacetic acid did not modify the effects of Ebs or (PhSe)(2) on the mitochondria. Additionally, Ebs and (PhSe)(2) decreased the basal 2' 7' dichlorofluorescin diacetate (H(2)-DCFDA) oxidation and oxygen consumption rate in state 3 and increased it during the state 4 of oxidative phosphorylation and induced the formation of protein aggregates, which were prevented by DTT. However, DTT failed to reverse the formation of protein aggregates, when it was added after a preincubation of liver mitochondria with Ebs or (PhSe)(2). Similarly, DTT did not reverse the Ebs- or (PhSe)(2)-induced Deltapsim collapse or swelling, when it was added after a preincubation period of mitochondria with chalcogenides. These results show that Ebs and (PhSe)(2) can effectively induce mitochondrial dysfunction and suggest that effects of these compounds are associated with mitochondrial thiol groups oxidation. The inability of cyclosporine A to reverse the Ebs- and (PhSe)(2)-induced mitochondrial effects suggests that the redox-regulated mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) pore was mechanistically regulated in a manner that is distinct from the classical MPT pore.
Figures
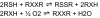


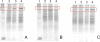
Similar articles
-
Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore by pyridine nucleotides and dithiol oxidation at two separate sites.J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):6746-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6746. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8636095
-
Alteration in mitochondrial thiol enhances calcium ion dependent membrane permeability transition and dysfunction in vitro: a cross-talk between mtThiol, Ca(2+), and ROS.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Nov;357(1-2):373-85. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0908-0. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21748338
-
Sulfite disrupts brain mitochondrial energy homeostasis and induces mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening via thiol group modification.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1842(9):1413-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24793416
-
Effects of Tl+ on the inner membrane thiol groups, respiration, and swelling in succinate-energized rat liver mitochondria were modified by thiol reagents.Biometals. 2021 Oct;34(5):987-1006. doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00329-6. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Biometals. 2021. PMID: 34236558 Review.
-
The mitochondrial permeability transition from yeast to mammals.FEBS Lett. 2010 Jun 18;584(12):2504-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.023. Epub 2010 Apr 14. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20398660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicology and pharmacology of synthetic organoselenium compounds: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Apr;95(4):1179-1226. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03003-5. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33792762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organochalcogens inhibit mitochondrial complexes I and II in rat brain: possible implications for neurotoxicity.Neurotox Res. 2013 Aug;24(2):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9365-0. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Neurotox Res. 2013. PMID: 23224748 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism(s) of Toxic Action of Zn and Selenite: A Study on AS-30D Hepatoma Cells and Isolated Mitochondria.Biochem Res Int. 2011;2011:387297. doi: 10.1155/2011/387297. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Biochem Res Int. 2011. PMID: 21860797 Free PMC article.
-
New therapeutic approach: diphenyl diselenide reduces mitochondrial dysfunction in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e81961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081961. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349162 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cell lines by ebselen via enhancing the endogenous reactive oxygen species production.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:696107. doi: 10.1155/2014/696107. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24587987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardais AP, Viola GG, Costa MS, Nunes F, Behr GA, Klamt F, Moreira JC, Souza DO, Rocha JBT, Porciúncula LO. Acute treatment with diphenyl diselenide inhibits glutamate uptake into rat hippocampal slices and modifies glutamate transporters, SNAP-25, and GFAP immunocontent. Toxicol. Sci. 2010;113:434–443. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa NBV, Rocha JBT, Soares JCM, Wondracek DC, Goncalves JF, Schetinger MRC, Nogueira CW. Dietary diphenyl diselenide reduces the STZ-induced toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008;46:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Beatrice MC, Palmer JW, Pfeiffer DR. The relationship between mitochondrial membrane permeability, membrane potential, and the retention of Ca2+ by mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:8663–8671. - PubMed
-
- Brand MD, Affourtit C, Esteves TC, Green K, Lambert AJ, Miwa S, Pakay JL, Parker N. Mitochondrial superoxide: production, biological effects, and activation of uncoupling proteins. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004;37:755–767. - PubMed
-
- Brito VB, Folmer V, Puntel GO, Fachinetto R, Soares JCM, Zeni G, Nogueira CW, Rocha JBT. Diphenyl diselenide and 2,3-dimercaptopropanol increase the PTZ-induced chemical seizure and mortality in mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2006;68:414–418. - PubMed

