Dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein 6 is required for normal electrophysiological properties of cerebellar granule cells
- PMID: 20573902
- PMCID: PMC2916862
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5489-09.2010
Dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein 6 is required for normal electrophysiological properties of cerebellar granule cells
Abstract
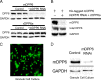
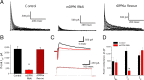
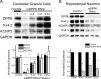
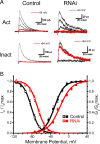
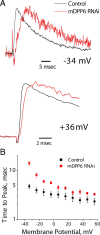
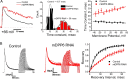
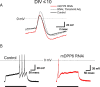
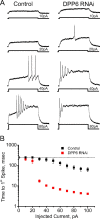
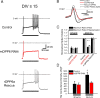
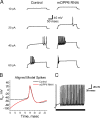
In cerebellar granule (CG) cells and many other neurons, A-type potassium currents play an important role in regulating neuronal excitability, firing patterns, and activity-dependent plasticity. Protein biochemistry has identified dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein 6 (DPP6) as an auxiliary subunit of Kv4-based A-type channels and thus a potentially important regulator of neuronal excitability. In this study, we used an RNA interference (RNAi) strategy to examine the role DPP6 plays in forming and shaping the electrophysiological properties of CG cells. DPP6 RNAi delivered by lentiviral vectors effectively disrupts DPP6 protein expression in CG cells. In response to the loss of DPP6, I(SA) peak conductance amplitude is reduced by >85% in parallel with a dramatic reduction in the level of I(SA) channel protein complex found in CG cells. The I(SA) channels remaining in CG cells after suppression of DPP6 show alterations in gating similar to Kv4 channels expressed in heterologous systems without DPP6. In addition to these effects on A-type current, we find that loss of DPP6 has additional effects on input resistance and Na(+) channel conductance that combine with the effects on I(SA) to produce a global change in excitability. Overall, DPP6 expression seems to be critical for the expression of a high-frequency electrophysiological phenotype in CG cells by increasing leak conductance, A-type current levels and kinetics, and Na(+) current amplitude.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new TASK for Dipeptidyl Peptidase-like Protein 6.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e60831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060831. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593319 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporation of DPP6a and DPP6K variants in ternary Kv4 channel complex reconstitutes properties of A-type K current in rat cerebellar granule cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038205. Epub 2012 Jun 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22675523 Free PMC article.
-
A novel DPP6 isoform (DPP6-E) can account for differences between neuronal and reconstituted A-type K(+) channels.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Jan 16;449(3):189-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.098. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19007856 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Roles of the Multifunctional Protein Dipeptidyl Peptidase-like 6 (DPP6).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 16;23(16):9184. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169184. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weighing the evidence for a ternary protein complex mediating A-type K+ currents in neurons.J Physiol. 2008 Dec 1;586(23):5609-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.161620. Epub 2008 Oct 9. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18845608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A-Type KV Channels in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons: Diversity, Function, and Dysfunction.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Aug 6;11:253. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00253. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30127716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DPP6 domains responsible for its localization and function.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 14;289(46):32153-32165. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.578070. Epub 2014 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25190807 Free PMC article.
-
Transient outward potassium channel: a heart failure mediator.Heart Fail Rev. 2015 May;20(3):349-62. doi: 10.1007/s10741-015-9474-y. Heart Fail Rev. 2015. PMID: 25646587 Review.
-
Kv4.2 and accessory dipeptidyl peptidase-like protein 10 (DPP10) subunit preferentially form a 4:2 (Kv4.2:DPP10) channel complex.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 11;290(37):22724-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646794. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26209633 Free PMC article.
-
The sodium channel accessory subunit Navβ1 regulates neuronal excitability through modulation of repolarizing voltage-gated K⁺ channels.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 25;32(17):5716-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6450-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22539834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aamodt SM, Constantine-Paton M. The role of neural activity in synaptic development and its implications for adult brain function. Adv Neurol. 1999;79:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Alders M, Koopmann TT, Christiaans I, Postema PG, Beekman L, Tanck MW, Zeppenfeld K, Loh P, Koch KT, Demolombe S, Mannens MM, Bezzina CR, Wilde AA. Haplotype-sharing analysis implicates chromosome 7q36 harboring DPP6 in familial idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84:468–476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen M, Heinzmann A, Noguchi E, Abecasis G, Broxholme J, Ponting CP, Bhattacharyya S, Tinsley J, Zhang Y, Holt R, Jones EY, Lench N, Carey A, Jones H, Dickens NJ, Dimon C, Nicholls R, Baker C, Xue L, Townsend E, et al. Positional cloning of a novel gene influencing asthma from chromosome 2q14. Nat Genet. 2003;35:258–263. - PubMed
-
- An WF, Bowlby MR, Betty M, Cao J, Ling HP, Mendoza G, Hinson JW, Mattsson KI, Strassle BW, Trimmer JS, Rhodes KJ. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
