Neurons efficiently repair glutamate-induced oxidative DNA damage by a process involving CREB-mediated up-regulation of apurinic endonuclease 1
- PMID: 20573957
- PMCID: PMC2934684
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082883
Neurons efficiently repair glutamate-induced oxidative DNA damage by a process involving CREB-mediated up-regulation of apurinic endonuclease 1
Abstract
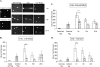
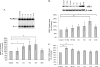
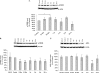
Glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, activates receptors coupled to membrane depolarization and Ca(2+) influx that mediates functional responses of neurons including processes such as learning and memory. Here we show that reversible nuclear oxidative DNA damage occurs in cerebral cortical neurons in response to transient glutamate receptor activation using non-toxic physiological levels of glutamate. This DNA damage was prevented by intracellular Ca(2+) chelation, the mitochondrial superoxide dismutase mimetic MnTMPyP (Mn-5,10,15,20-tetra(4-pyridyl)-21H,23H-porphine chloride tetrakis(methochloride)), and blockade of the permeability transition pore. The repair of glutamate-induced DNA damage was associated with increased DNA repair activity and increased mRNA and protein levels of apurinic endonuclease 1 (APE1). APE1 knockdown induced accumulation of oxidative DNA damage after glutamate treatment, suggesting that APE1 is a key repair protein for glutamate-induced DNA damage. A cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) binding sequence is present in the Ape1 gene (encodes APE1 protein) promoter and treatment of neurons with a Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase inhibitor (KN-93) blocked the ability of glutamate to induce CREB phosphorylation and APE1 expression. Selective depletion of CREB using RNA interference prevented glutamate-induced up-regulation of APE1. Thus, glutamate receptor stimulation triggers Ca(2+)- and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-mediated DNA damage that is then rapidly repaired by a mechanism involving Ca(2+)-induced, CREB-mediated APE1 expression. Our findings reveal a previously unknown ability of neurons to efficiently repair oxidative DNA lesions after transient activation of glutamate receptors.
Figures

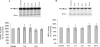

Similar articles
-
BDNF and exercise enhance neuronal DNA repair by stimulating CREB-mediated production of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1.Neuromolecular Med. 2014 Mar;16(1):161-174. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8270-x. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Neuromolecular Med. 2014. PMID: 24114393 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative DNA damage is concurrently repaired by base excision repair (BER) and apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1)-initiated nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) in cortical neurons.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020 Jun;46(4):375-390. doi: 10.1111/nan.12584. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31628877 Free PMC article.
-
The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate stimulates DNA repair to increase neuronal resiliency.Mech Ageing Dev. 2011 Aug;132(8-9):405-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.005. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Mech Ageing Dev. 2011. PMID: 21729715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of GLP-1 Receptor Enhances Neuronal Base Excision Repair via PI3K-AKT-Induced Expression of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1.Theranostics. 2016 Sep 2;6(12):2015-2027. doi: 10.7150/thno.15993. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 27698937 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA base excision repair protein Ape1/Ref-1 as a therapeutic and chemopreventive target.Mol Aspects Med. 2007 Jun-Aug;28(3-4):375-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 3. Mol Aspects Med. 2007. PMID: 17560642 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of DNA Damage in Neural Plasticity in Physiology and Neurodegeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 23;16:836885. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.836885. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: An in-depth review.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 1;16:970925. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.970925. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36117625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress-induced CREB upregulation promotes DNA damage repair prior to neuronal cell death protection.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Jan;425(1-2):9-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2858-z. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27816995
-
Changes in mitochondrial function are pivotal in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders: how important is BDNF?Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(8):2206-29. doi: 10.1111/bph.12531. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24720259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the effects of endurance exercise to optimize cognitive health: Fundamental insights from Dr. Mark P. Mattson.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Dec;64:101147. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101147. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32814127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

