Nix is critical to two distinct phases of mitophagy, reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy induction and Parkin-ubiquitin-p62-mediated mitochondrial priming
- PMID: 20573959
- PMCID: PMC2934655
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.119537
Nix is critical to two distinct phases of mitophagy, reactive oxygen species-mediated autophagy induction and Parkin-ubiquitin-p62-mediated mitochondrial priming
Abstract
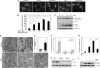
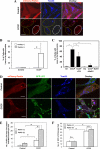
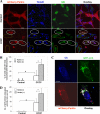
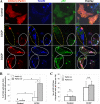
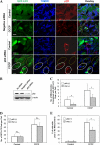
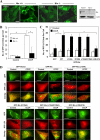
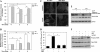
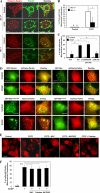
Damaged mitochondria can be eliminated by autophagy, i.e. mitophagy, which is important for cellular homeostasis and cell survival. Despite the fact that a number of factors have been found to be important for mitophagy in mammalian cells, their individual roles in the process had not been clearly defined. Parkin is a ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase able to translocate to the mitochondria that are to be removed. We showed here in a chemical hypoxia model of mitophagy induced by an uncoupler, carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) that Parkin translocation resulted in mitochondrial ubiquitination and p62 recruitment to the mitochondria. Small inhibitory RNA-mediated knockdown of p62 significantly diminished mitochondrial recognition by the autophagy machinery and the subsequent elimination. Thus Parkin, ubiquitin, and p62 function in preparing mitochondria for mitophagy, here referred to as mitochondrial priming. However, these molecules were not required for the induction of autophagy machinery. Neither Parkin nor p62 seemed to affect autophagy induction by CCCP. Instead, we found that Nix was required for the autophagy induction. Nix promoted CCCP-induced mitochondrial depolarization and reactive oxygen species generation, which inhibited mTOR signaling and activated autophagy. Nix also contributed to mitochondrial priming by controlling the mitochondrial translocation of Parkin, although reactive oxygen species generation was not involved in this step. Deletion of the C-terminal membrane targeting sequence but not mutations in the BH3 domain disabled Nix for these functions. Our work thus distinguished the molecular events responsible for the different phases of mitophagy and placed Nix upstream of the events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clearance of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy is important to the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning in kidneys.Autophagy. 2019 Dec;15(12):2142-2162. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1615822. Epub 2019 May 22. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 31066324 Free PMC article.
-
p62/SQSTM1 is required for Parkin-induced mitochondrial clustering but not mitophagy; VDAC1 is dispensable for both.Autophagy. 2010 Nov;6(8):1090-106. doi: 10.4161/auto.6.8.13426. Autophagy. 2010. PMID: 20890124 Free PMC article.
-
Parkin-induced ubiquitination of Mff promotes its association with p62/SQSTM1 during mitochondrial depolarization.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015 Jul;47(7):522-9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv044. Epub 2015 May 24. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2015. PMID: 26008206
-
The reciprocal roles of PARK2 and mitofusins in mitophagy and mitochondrial spheroid formation.Autophagy. 2013 Nov 1;9(11):1687-92. doi: 10.4161/auto.24871. Epub 2013 May 21. Autophagy. 2013. PMID: 24162069 Review.
-
N-degron-mediated degradation and regulation of mitochondrial PINK1 kinase.Curr Genet. 2020 Aug;66(4):693-701. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01062-2. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32157382 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondria and mitophagy: the yin and yang of cell death control.Circ Res. 2012 Oct 12;111(9):1208-21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.265819. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 23065344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide induced mitophagy and tumor suppression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt B):2834-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.12.039. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25634657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PINK1 Is Dispensable for Mitochondrial Recruitment of Parkin and Activation of Mitophagy in Cardiac Myocytes.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 25;10(6):e0130707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130707. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26110811 Free PMC article.
-
Proximity Ligation In situ Assay is a Powerful Tool to Monitor Specific ATG Protein Interactions following Autophagy Induction.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 2;10(6):e0128701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128701. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26034986 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting autophagy for the treatment of liver diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Dec;66(6):463-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.07.003. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22871337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

