Differential proteomics analysis reveals a role for E2F2 in the regulation of the Ahr pathway in T lymphocytes
- PMID: 20573986
- PMCID: PMC2953915
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.001263
Differential proteomics analysis reveals a role for E2F2 in the regulation of the Ahr pathway in T lymphocytes
Abstract
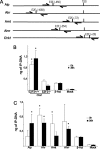
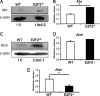
E2F transcription factors (E2F1-8) are best known for their role in cell proliferation, although it is clear that they regulate many other biological processes through the transcriptional modulation of distinct target genes. However, the specific set of genes regulated by each E2F remains to be characterized. To gain insight into the molecular pathways regulated by E2F2, we have analyzed the proteome of antigen receptor-activated T cells lacking E2F2. We report that loss of E2F2 results in a deregulated Aryl-hydrocarbon-receptor pathway. Proliferating E2F2(-/-) T lymphocytes expressed significantly higher levels of Aip, Ahr, and Arnt relative to wild-type (WT)(1) controls. The mechanism for increased levels of Aip appears straightforward, involving direct regulation of the Aip gene promoter by E2F2. Although the Ahr and Arnt promoters also bind E2F2, their regulation appears to be more complex. Nevertheless, exposure to the environmental xenobiotic 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a well-known exogenous ligand of the Ahr pathway, led to overexpression of the Ahr target gene Cyp1a1, and to increased sensitivity to TCDD-triggered apoptosis in E2F2(-/-) T cells compared with WT controls. These results suggest that E2F2 modulates cellular sensitivity to xenobiotic signals through the negative regulation of the Ahr pathway.
Figures





Similar articles
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 through an aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathway in mouse hepatoma cell lines.Arch Toxicol. 2002 Jul;76(7):404-13. doi: 10.1007/s00204-002-0354-6. Epub 2002 May 16. Arch Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12111005
-
RT-PCR quantification of AHR, ARNT, GR, and CYP1A1 mRNA in craniofacial tissues of embryonic mice exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and hydrocortisone.Toxicol Sci. 1999 Jan;47(1):76-85. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/47.1.76. Toxicol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10048155
-
Treatment of mice with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin leads to aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and expression of Fas ligand in thymic stromal cells and consequent apoptosis in T cells.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 1;175(1):90-103. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.90. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15972635
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent suppression by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin of IgM secretion in activated B cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Apr;53(4):623-9. Mol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9547351
-
Transcriptional regulation of innate lymphoid cells and T cells by aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 28;14:1056267. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1056267. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37056785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nuclear protein ALY binds to and modulates the activity of transcription factor E2F2.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 May;12(5):1087-98. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.024158. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23297349 Free PMC article.
-
E2F1/2/4 mRNA is associated with immune infiltration and are potential biomarkers for the prognosis of human gastric carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;10(6):2801-2811. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-45. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116590 Free PMC article.
-
E2F2 inhibition induces autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 21;13(10):13626-13643. doi: 10.18632/aging.202891. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34091441 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of E2F2 Expression in Governing Endothelial Cell Senescence.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 24;13(9):1522. doi: 10.3390/genes13091522. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140689 Free PMC article.
-
Multigenerational and Transgenerational Effects of Dioxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2947. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122947. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dyson N. (1998) The regulation of E2F by pRBfamily proteins. Genes Dev. 12, 2245–2262 - PubMed
-
- DeGregori J., Johnson D. G. (2006) Distinct and overlapping roles for E2F family members in transcription, proliferation and apoptosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 6, 739–748 - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T., Ono T., Kitamura N., Kato J. Y. (2003) Dominant negative E2F inhibits progression of the cell cycle after the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Cell Struct. Funct. 28, 515–522 - PubMed
-
- Yang Q., Hu J., Ye D., Zhao C., Song S., Gong W., Tan Z., Song P. (2010) Identification and expression analysis of two zebrafish E2F5 genes during oogenesis and development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 37, 1773–1780 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

