Reproducibility of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography total retinal thickness measurements in mice
- PMID: 20574022
- PMCID: PMC3055768
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-5662
Reproducibility of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography total retinal thickness measurements in mice
Abstract
Purpose: To test the reproducibility of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) total retinal thickness (TRT) measurements in mice.
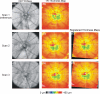
Methods: C57Bl/6 mice were anesthetized, and three repeated volumetric images were acquired in both eyes with SD-OCT (250 A-scans × 250 frames × 1024 samplings), centered on the optic nerve head (ONH). The mice were repositioned between scans. TRT was automatically measured within a sampling band of retinal thickness with radii of 55 to 70 pixels, centered on the ONH by using custom segmentation software. The first volumetric image acquired in a given eye was used to register the remaining two SD-OCT images by manually aligning the en face images with respect to rotation and linear translation. Linear mixed-effects models were fitted to global and quadrant thicknesses, taking into account the clustering between eyes, to assess imprecision (measurement reproducibility).
Results: Twenty-six eyes of 13 adult mice (age 13 weeks) were imaged. The mean global TRT across all eyes was 298.21 μm, with a mouse heterogeneity standard deviation (SD) of 4.88 μm (coefficient of variation [CV] = 0.016), an eye SD of 3.32 μm (CV = 0.011), and a device-related imprecision SD of 2.33 μm (CV = 0.008). The superior quadrant had the thickest mean TRT measurement (310.38 μm) and the highest (worst) imprecision SD (3.13 μm; CV = 0.010), and the inferior quadrant had the thinnest mean TRT (291.55 μm). The quadrant with the lowest (best) imprecision SD was in the nasal one (2.06 μm; CV = 0.007).
Conclusions: Good reproducibility was observed for SD-OCT retinal thickness measurements in mice. SD-OCT may be useful for in vivo longitudinal studies in mice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optic nerve crush mice followed longitudinally with spectral domain optical coherence tomography.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Apr 6;52(5):2250-4. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6311. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21398282 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability and Reproducibility of Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Measurements of Retinal Thickness in Rats.Curr Eye Res. 2016 Oct;41(10):1346-1352. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2015.1114651. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Curr Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26862705
-
Retinal thickness measurement obtained with spectral domain optical coherence tomography assisted optical biopsy accurately correlates with ex vivo histology.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 31;9(10):e111203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111203. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25360629 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of manually corrected retinal thickness measurements from multiple spectral-domain optical coherence tomography instruments.Br J Ophthalmol. 2012 Mar;96(3):380-5. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2010.201111. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 21733920
-
Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) assessment of the healthy female canine retina and optic nerve.Vet Ophthalmol. 2011 Nov;14(6):400-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2011.00887.x. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Vet Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 22050777 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of in vivo confocal autofluorescence imaging of the ocular fundus in mice and its application to models of human retinal degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Feb 29;53(2):1066-75. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8767. Print 2012 Feb. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22169101 Free PMC article.
-
A combined machine-learning and graph-based framework for the segmentation of retinal surfaces in SD-OCT volumes.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Nov 1;4(12):2712-28. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.002712. eCollection 2013. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24409375 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive optics optical coherence tomography for in vivo mouse retinal imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2013 May;18(5):56007. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.5.056007. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23644903 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and morphological analysis of the subretinal injection of retinal pigment epithelium cells.Vis Neurosci. 2012 Mar;29(2):83-93. doi: 10.1017/S0952523812000041. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Vis Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22391151 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography: history, current status, and laboratory work.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Apr 14;52(5):2425-36. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6312. Print 2011 Apr. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21493951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baumann M, Gentile RC, Liebmann JM, Ritch R. Reproducibility of retinal thickness measurements in normal eyes using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1998;29:280–285 - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal EZ, Williams JM, Weinreb RN, Girkin CA, Berry CC, Zangwill LM. Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements by use of optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:2278–2282 - PubMed
-
- Massin P, Vicaut E, Haouchine B, Erginay A, Paques M, Gaudric A. Reproducibility of retinal mapping using optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001;119:1135–1142 - PubMed
-
- Gurses-Ozden R, Teng C, Vessani R, Zafar S, Liebmann JM, Ritch R. Macular and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement reproducibility using optical coherence tomography (OCT-3). J Glaucoma. 2004;13:238–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

