Effective and sustained delivery of hydrophobic retinoids to photoreceptors
- PMID: 20574023
- PMCID: PMC3061517
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-5766
Effective and sustained delivery of hydrophobic retinoids to photoreceptors
Abstract
Purpose: Delivery of hydrophobic compounds to the retina/RPE has been challenging. The purpose of this study was to develop an effective method for the sustained delivery of retinoids to rod and cone photoreceptors of young mice lacking a normal supply of 11-cis retinal.
Methods: Solubilized basement membrane matrix (Matrigel; BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) loaded with 9-cis retinal was administered subcutaneously into Rpe65(-/-) mouse pups for assessment of delivery to rods and cones and to Rpe65(-/-)Rho(-/-) mouse pups for assessment of delivery to cones. Intraperitoneal injections of 9-cis retinal were used for comparison. Cone density and opsin localization were evaluated with immunohistochemistry. Cone opsin protein levels were assayed with immunoblots, and cone function was analyzed by electroretinography (ERG) recordings. Retinoid content was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of retinal extracts. Pigment levels were quantified in homogenized retinas by absorption spectroscopy before and after light exposure.
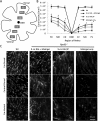
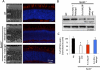
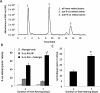
Results: Single administration of Matrigel loaded with 9-cis retinal to Rpe65(-/-) mice increased cone densities in all analyzed regions of the retina compared with mice treated using intraperitoneal delivery. Cone opsin levels increased to near wild-type levels. Similar treatment in Rpe65(-/-)Rho(-/-) mice increased b-wave ERG amplitudes significantly, indicating the maintenance of cone function. Matrigel was shown to continuously release 9-cis retinal for periods up to 1 week.
Conclusions: As a method for sustained drug delivery, subcutaneous administration using Matrigel proved more efficacious than intraperitoneal injection for in vivo delivery of retinoids to cone photoreceptors. These experiments are the first to show a sustained delivery of retinoids in mice and suggest a strategy for potential clinical therapeutic development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nrl-knockout mice deficient in Rpe65 fail to synthesize 11-cis retinal and cone outer segments.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Mar;49(3):1126-35. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1234. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18326740 Free PMC article.
-
Light prevents exogenous 11-cis retinal from maintaining cone photoreceptors in chromophore-deficient mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Apr 14;52(5):2412-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6437. Print 2011 Apr. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21228385 Free PMC article.
-
Cone opsin mislocalization in Rpe65-/- mice: a defect that can be corrected by 11-cis retinal.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Oct;46(10):3876-82. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0533. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16186377
-
Vitamin A and Vision.Subcell Biochem. 2016;81:231-259. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0945-1_9. Subcell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27830507 Review.
-
The visual cycle of the cone photoreceptors of the retina.Nutr Rev. 2004 Jul;62(7 Pt 1):283-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2004.tb00053.x. Nutr Rev. 2004. PMID: 15384919 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox-Responsive Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanogels for the Topical Delivery of the Visual Chromophore to Retinal Photoreceptors.ACS Omega. 2021 Feb 22;6(9):6172-6184. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05535. eCollection 2021 Mar 9. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33718708 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced osseous integration of human trabecular allografts following surface modification with bioactive lipids.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016 Apr;6(2):96-104. doi: 10.1007/s13346-015-0244-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 26169381 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Leads to RPE65 Decrease and Retinal Degeneration.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Nov 28;37(24):e00295-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00295-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 29038159 Free PMC article.
-
The use of Matrigel combined with encapsulated cell technology to deliver a complement inhibitor in a mouse model of choroidal neovascularization.Mol Vis. 2020 May 15;26:370-377. eCollection 2020. Mol Vis. 2020. PMID: 32476817 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of Fatty Acid Transport Protein-4 Enhances Cone Survival, M-cone Vision, and Synthesis of Cone-Tropic 9-cis-Retinal in rd12 Mouse Model of Leber Congenital Amaurosis.J Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;44(27):e1994232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1994-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38811164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geroski DH, Edelhauser HF. Drug delivery for posterior segment eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:961–964 - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi MA, Lim JI. Pharmacotherapy of age-related macular degeneration. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9:3045–3052 - PubMed
-
- Le-Goff MM, Bishop PN. Adult vitreous structure and postnatal changes. Eye. 2008;22:1214–1222 - PubMed
-
- Cruysberg LP, Nuijts RM, Gilbert JA, Geroski DH, Hendrikse F, Edelhauser HF. Delivery of fluorescein-labeled dexamethasone and methotrexate with fibrin sealant. Curr Eye Res. 2005;30:653–660 - PubMed
-
- Hsiue GH, Chang RW, Wang CH, Lee SH. Development of in situ thermosensitive drug vehicles for glaucoma therapy. Biomaterials. 2003;24:2423–2430 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

