Crucial roles of B7-H1 and B7-DC expressed on mesenteric lymph node dendritic cells in the generation of antigen-specific CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the establishment of oral tolerance
- PMID: 20574047
- PMCID: PMC3368550
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-10-250472
Crucial roles of B7-H1 and B7-DC expressed on mesenteric lymph node dendritic cells in the generation of antigen-specific CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the establishment of oral tolerance
Abstract
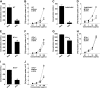
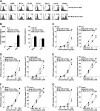
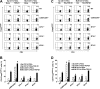
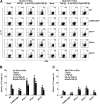
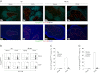
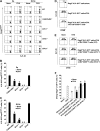
Oral tolerance is a key feature of intestinal immunity, generating systemic tolerance to fed antigens. However, the molecular mechanism mediating oral tolerance remains unclear. In this study, we examined the role of the B7 family members of costimulatory molecules in the establishment of oral tolerance. Deficiencies of B7-H1 and B7-DC abrogated the oral tolerance, accompanied by enhanced antigen-specific CD4(+) T-cell response and IgG(1) production. Mesenteric lymph node (MLN) dendritic cells (DCs) displayed higher levels of B7-H1 and B7-DC than systemic DCs, whereas they showed similar levels of CD80, CD86, and B7-H2. MLN DCs enhanced the antigen-specific generation of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) inducible regulatory T cells (iT(regs)) from CD4(+)Foxp3(-) T cells rather than CD4(+) effector T cells (T(eff)) relative to systemic DCs, owing to the dominant expression of B7-H1 and B7-DC. Furthermore, the antigen-specific conversion of CD4(+)Foxp3(-) T cells into CD4(+)Foxp3(+) iT(regs) occurred in MLNs greater than in peripheral organs during oral tolerance under steady-state conditions, and such conversion required B7-H1 and B7-DC more than other B7 family members, whereas it was severely impaired under inflammatory conditions. In conclusion, our findings suggest that B7-H1 and B7-DC expressed on MLN DCs are essential for establishing oral tolerance through the de novo generation of antigen-specific CD4(+)Foxp3(+) iT(regs).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

