Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR-4-activated macrophages
- PMID: 20574076
- PMCID: PMC2918461
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M008748
Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR-4-activated macrophages
Abstract
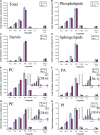
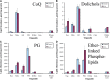
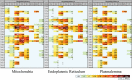
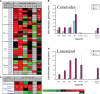
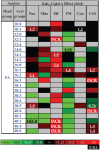
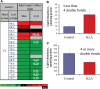
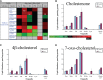
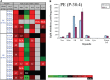
Lipids orchestrate biological processes by acting remotely as signaling molecules or locally as membrane components that modulate protein function. Detailed insight into lipid function requires knowledge of the subcellular localization of individual lipids. We report an analysis of the subcellular lipidome of the mammalian macrophage, a cell type that plays key roles in inflammation, immune responses, and phagocytosis. Nuclei, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), plasmalemma, and cytoplasm were isolated from RAW 264.7 macrophages in basal and activated states. Subsequent lipidomic analyses of major membrane lipid categories identified 229 individual/isobaric species, including 163 glycerophospholipids, 48 sphingolipids, 13 sterols, and 5 prenols. Major subcellular compartments exhibited substantially divergent glycerophospholipid profiles. Activation of macrophages by the Toll-like receptor 4-specific lipopolysaccharide Kdo(2)-lipid A caused significant remodeling of the subcellular lipidome. Some changes in lipid composition occurred in all compartments (e.g., increases in the levels of ceramides and the cholesterol precursors desmosterol and lanosterol). Other changes were manifest in specific organelles. For example, oxidized sterols increased and unsaturated cardiolipins decreased in mitochondria, whereas unsaturated ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamines decreased in the ER. We speculate that these changes may reflect mitochondrial oxidative stress and the release of arachidonic acid from the ER in response to cell activation.
Figures

References
-
- Wymann M. P., Schneiter R. 2008. Lipid signalling in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 162–176. - PubMed
-
- Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. 2008. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 139–150. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls D. G. 2006. The physiological regulation of uncoupling proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1757: 459–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

