The de-ubiquitinase UCH-L1 is an oncogene that drives the development of lymphoma in vivo by deregulating PHLPP1 and Akt signaling
- PMID: 20574456
- PMCID: PMC3236611
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2010.138
The de-ubiquitinase UCH-L1 is an oncogene that drives the development of lymphoma in vivo by deregulating PHLPP1 and Akt signaling
Abstract
De-ubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) can reverse the modifications catalyzed by ubiquitin ligases and as such are believed to be important regulators of a variety of cellular processes. Several members of this protein family have been associated with human cancers; however, there is little evidence for a direct link between deregulated de-ubiquitination and neoplastic transformation. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase (UCH)-L1 is a DUB of unknown function that is overexpressed in several human cancers, but whether it has oncogenic properties has not been established. To address this issue, we generated mice that overexpress UCH-L1 under the control of a ubiquitous promoter. Here, we show that UCH-L1 transgenic mice are prone to malignancy, primarily lymphomas and lung tumors. Furthermore, UCH-L1 overexpression strongly accelerated lymphomagenesis in Emu-myc transgenic mice. Aberrantly expressed UCH-L1 boosts signaling through the Akt pathway by downregulating the antagonistic phosphatase PHLPP1, an event that requires its de-ubiquitinase activity. These data provide the first in vivo evidence for DUB-driven oncogenesis and suggest that UCH-L1 hyperactivity deregulates normal Akt signaling.
Figures

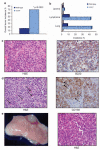
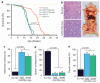
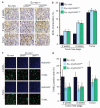
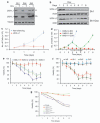
Similar articles
-
UCH-L1 promotes invasion of breast cancer cells through activating Akt signaling pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jan;119(1):691-700. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26232. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28636190 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of ubiquitin carboxy terminal hydrolase-L1 induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2008 Nov;33(5):1037-45. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000092. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18949367 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin hydrolase UCH-L1 destabilizes mTOR complex 1 by antagonizing DDB1-CUL4-mediated ubiquitination of raptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;33(6):1188-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01389-12. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23297343 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1): structure, distribution and roles in brain function and dysfunction.Biochem J. 2016 Aug 15;473(16):2453-62. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160082. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27515257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolases: involvement in cancer progression and clinical implications.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Dec;36(4):669-682. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9702-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 29080080 Review.
Cited by
-
UCHL1 Promoted Polarization of M1 Macrophages by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 4;15:735-746. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S343487. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35153498 Free PMC article.
-
PU.1-dependent regulation of UCH L1 expression in B-lymphoma cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Jul;52(7):1336-47. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.562571. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21504384 Free PMC article.
-
Role of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible α in Akt phosphorylation and ubiquitination after mechanical stress-induced vascular injury.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 1;184(9):1030-40. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201103-0447OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21816939 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PHLPP1 ameliorates cardiac dysfunction via activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in diabetic cardiomyopathy.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(8):4612-4623. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15123. Epub 2020 Mar 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32150791 Free PMC article.
-
UCH-L1 in DLBCL: marker or target?Blood. 2016 Mar 24;127(12):1524-5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-689984. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27013211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoeller D, Hecker CM, Dikic I. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:776–788. - PubMed
-
- Glickman MH, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:373–428. - PubMed
-
- Nijman SM, Luna-Vargas MP, Velds A, Brummelkamp TR, Dirac AM, Sixma TK, et al. A genomic and functional inventory of deubiquitinating enzymes. Cell. 2005;123:773–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

