The early nutritional environment of mice determines the capacity for adipose tissue expansion by modulating genes of caveolae structure
- PMID: 20574519
- PMCID: PMC2888576
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011015
The early nutritional environment of mice determines the capacity for adipose tissue expansion by modulating genes of caveolae structure
Abstract
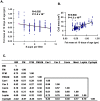
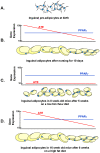
While the phenomenon linking the early nutritional environment to disease susceptibility exists in many mammalian species, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. We hypothesized that nutritional programming is a variable quantitative state of gene expression, fixed by the state of energy balance in the neonate, that waxes and wanes in the adult animal in response to changes in energy balance. We tested this hypothesis with an experiment, based upon global gene expression, to identify networks of genes in which expression patterns in inguinal fat of mice have been altered by the nutritional environment during early post-natal development. The effects of over- and under-nutrition on adiposity and gene expression phenotypes were assessed at 5, 10, 21 days of age and in adult C57Bl/6J mice fed chow followed by high fat diet for 8 weeks. Under-nutrition severely suppressed plasma insulin and leptin during lactation and diet-induced obesity in adult mice, whereas over-nourished mice were phenotypically indistinguishable from those on a control diet. Food intake was not affected by under- or over-nutrition. Microarray gene expression data revealed a major class of genes encoding proteins of the caveolae and cytoskeleton, including Cav1, Cav2, Ptrf (Cavin1), Ldlr, Vldlr and Mest, that were highly associated with adipose tissue expansion in 10 day-old mice during the dynamic phase of inguinal fat development and in adult animals exposed to an obesogenic environment. In conclusion gene expression profiles, fat mass and adipocyte size in 10 day old mice predicted similar phenotypes in adult mice with variable diet-induced obesity. These results are supported by phenotypes of KO mice and suggest that when an animal enters a state of positive energy balance adipose tissue expansion is initiated by coordinate changes in mRNA levels for proteins required for modulating the structure of the caveolae to maximize the capacity of the adipocyte for lipid storage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


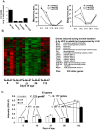
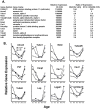
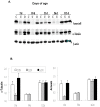
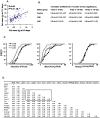
References
-
- Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP, Nadeau A, Lupien PJ, et al. The response to long-term overfeeding in identical twins. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1477–1482. - PubMed
-
- Allison DB, Kaprio J, Korkeila M, Koskenvuo M, Neale MC, et al. The heritability of body mass index among an international sample of monozygotic twins reared apart. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996;20:501–506. - PubMed
-
- Barsh GS, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature. 2000;404:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Reed GW, Peters JC. Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science. 2003;299:853–855. - PubMed
-
- Levine JA, Eberhardt NL, Jensen MD. Role of nonexercise activity thermogenesis in resistance to fat gain in humans [see comments]. Science. 1999;283:212–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

