Microbubble Compositions, Properties and Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 20574549
- PMCID: PMC2889676
- DOI: 10.1179/175889709X446507
Microbubble Compositions, Properties and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
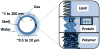
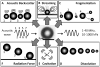
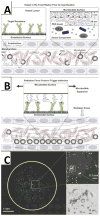
Over the last decade, there has been significant progress towards the development of microbubbles as theranostics for a wide variety of biomedical applications. The unique ability of microbubbles to respond to ultrasound makes them useful agents for contrast ultrasound imaging, molecular imaging, and targeted drug and gene delivery. The general composition of a microbubble is a gas core stabilized by a shell comprised of proteins, lipids or polymers. Each type of microbubble has its own unique advantages and can be tailored for specialized functions. In this review, different microbubbles compositions and physiochemical properties are discussed in the context of current progress towards developing novel constructs for biomedical applications, with specific emphasis on molecular imaging and targeted drug/gene delivery.
Figures
References
-
- Unger EC, Porter T, Culp W, Labell R, Matsunaga T, Zutshi R. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2004;56:1291–1314. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara K, Pollard R, Borden M. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2007;9:415–447. - PubMed
-
- Lindner JR. Nature Rev Drug Discovery. 2004;3:527–532. - PubMed
-
- Feinstein SB. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:H450–H457. - PubMed
-
- Dayton PA, Rychak JJ. Frontiers in Bioscience. 2007;12:5124–5142. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
