Effects of epigallocatechin gallate, L-ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and dihydrolipoic acid on the formation of deoxyguanosine adducts derived from lipid peroxidation
- PMID: 20574923
- PMCID: PMC3764924
- DOI: 10.1080/01635580903532424
Effects of epigallocatechin gallate, L-ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and dihydrolipoic acid on the formation of deoxyguanosine adducts derived from lipid peroxidation
Abstract
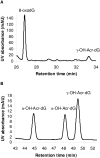
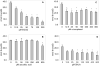
Oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) releases alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes that modify deoxyguanosine (dG) to form cyclic 1,N(2)-propanodeoxyguanosine adducts. One of the major adducts detected in vivo is acrolein (Acr)-derived 1,N(2)-propanodeoxyguanosine (Acr-dG). We used a chemical model system to examine the effects of 4 antioxidants known to inhibit fatty acid oxidation on the formation of Acr-dG and 8-oxodeoxyguaonsine (8-oxodG) from the PUFA docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) under oxidative conditions. We found that epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA) inhibit both Acr-dG and 8-oxodG formation. In contrast, ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol actually increase Acr-dG at high concentrations and do not show a concentration-dependant inhibition of 8-oxodG. We also studied their effects on blocking Acr-dG formation directly from Acr. EGCG and DHLA can both effectively block Acr-dG formation, but ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol show weak or little effect. These results highlight the complexity of antioxidant mechanisms and also reveal that EGCG and DHLA are effective at suppressing lipid peroxidation-induced Acr-dG and 8-oxodG formation as well as blocking the reaction of dG with Acr.
Figures




References
-
- Nair U, Bartsch H, Nair J. Lipid peroxidation-induced DNA damage in cancer-prone inflammatory diseases: A review of published adduct types and levels in humans. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:1109–1120. - PubMed
-
- Nair J, De Flora S, Izzotti A, Bartsch H. Lipid peroxidation-derived etheno-DNA adducts in human atherosclerotic lesions. Mutat Res. 2007;621:95–105. - PubMed
-
- Marnett LJ. Oxy radicals, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage. Toxicology. 2002;181-182:219–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
