Skeletal dysplasias: evaluation with impulse oscillometry and thoracoabdominal motion analysis
- PMID: 20575094
- PMCID: PMC3338356
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.21246
Skeletal dysplasias: evaluation with impulse oscillometry and thoracoabdominal motion analysis
Abstract
Background: Children with skeletal dysplasia (SD) often have pulmonary disease, which can be life threatening. In clinical practice, chest wall and formal respiratory function tests are difficult to perform owing to the small size and cooperation. The objective of this study was to demonstrate distinct thoracopulmonary function patterns in children with SD.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study reviewing pulmonary function tests from 17 patients with the diagnosis of SD. Three subgroups were studied: Morquio syndrome (MS), metatropic-spondylocostal dysplasia (MSD), and unspecified skeletal dysplasias (SDU). Rib cage contribution to tidal volume excursions (%RC), phase angle (Phtheta), phase relation during total breath (PhRTB), respiratory resistance (Rrs(5-35) Hz), respiratory reactance (Xrs(5-35) Hz), resonant frequency, and their frequency-dependency were analyzed. Values were age-matched and height-matched to reference values of healthy subjects.
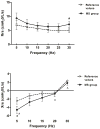
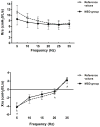
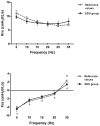
Results: There was a decrease in %RC and an increase in PhRTB (P < 0.05) in the SD group. %RC differed between subgroups [MS: 46.4 +/- 1.8% SE, MSD: 18.4 +/- 2.6% SE, SDU: 27.5 +/- 5.2% SE (P < 0.05)]; Phtheta was within reference values only in MS, which exhibited a decrease in Xrs at 5 Hz (P < 0.05) and an increase in Rrs independent of the frequency. SDU showed a decrease in Xrs at 35 Hz (P < 0.05), no differences were found in Rrs. In MS, a correlation was found between RC and Rrs at all frequencies (r = -0.98, P < 0.01) and between Xrs(5-10) and Phtheta (r = -0.93, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Thoracoabdominal dysfunction was associated with altered chest wall reactance at high frequencies in a subgroup of SD patients with abnormal lung reactance and central airway involvement in MS.
Figures
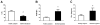
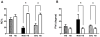
References
-
- Mogayzel PJ, Marcus CL. Skeletal dysplasias and their effect on the respiratory system. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2001;2(4):365–371. - PubMed
-
- Beydon N, Davis SD, Lombardi E, Allen JL, Arets HG, Aurora P, Bisgaard H, Davis GM, Ducharme FM, Eigen H, Gappa M, Gaultier C, Gustafsson PM, Hall GL, Hantos Z, Healy MJ, Jones MH, Klug B, Lodrup Carlsen KC, McKenzie SA, Marchal F, Mayer OH, Merkus PJ, Morris MG, Oostveen E, Pillow JJ, Seddon PC, Silverman M, Sly PD, Stocks J, Tepper RS, Vilozni D, Wilson NM. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: pulmonary function testing in preschool children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(12):1304–1345. - PubMed
-
- Nagels J, Landser FJ, van der Linden L, Clement J, Van de Woestijne KP. Mechanical properties of lungs and chest wall during spontaneous breathing. J Appl Physiol. 1980;49(3):408–416. - PubMed
-
- Allen JL, Wolfson MR, McDowell K, Shaffer TH. Thoracoabdominal asynchrony in infants with airflow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;141(2):337–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

