Sodium butyrate enhances the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin by abrogating the cisplatin imposed cell cycle arrest
- PMID: 20576112
- PMCID: PMC2906439
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-49
Sodium butyrate enhances the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin by abrogating the cisplatin imposed cell cycle arrest
Abstract
Background: Histone deacetylase inhibitors have been proposed as potential enhancers of the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin and other anticancer drugs. Their application would permit the use of lower therapeutic doses and reduction of the adverse side effects of the drugs. However, the molecular mechanisms by which they sensitize the cells towards anticancer drugs are not known in details, which is an obstacle in developing effective therapeutic protocols.
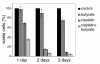
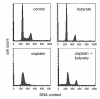
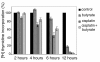
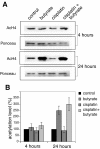
Results: In the present work, we studied the molecular mechanisms by which sodium butyrate sensitizes cancer cells towards cisplatin. HeLa cells were treated with 5 mM butyrate, with 8 microM cis-diaminedichloroplatinum II (cisplatin), or with both. Cells treated with both agents showed approximately two-fold increase of the mortality rate in comparison with cells treated with cisplatin only. Accordingly, the life span of albino mice transfected with Ehrlich ascites tumor was prolonged almost two-fold by treatment with cisplatin and butyrate in comparison with cisplatin alone. This showed that the observed synergism of cisplatin and butyrate was not limited to specific cell lines or in vitro protocols, but was also expressed in vivo during the process of tumor development. DNA labeling and fluorescence activated cell sorting experiments showed that cisplatin treatment inhibited DNA synthesis and arrested HeLa cells at the G1/S transition and early S phase of the cell cycle. Western blotting and chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that this effect was accompanied with a decrease of histone H4 acetylation levels. Butyrate treatment initially reversed the effect of cisplatin by increasing the levels of histone H4 acetylation in euchromatin regions responsible for the G1/S phase transition and initiation of DNA synthesis. This abrogated the cisplatin imposed cell cycle arrest and the cells traversed S phase with damaged DNA. However, this effect was transient and continued only a few hours. The long-term effect of butyrate was a massive histone acetylation in both eu- and heterochromatin, inhibition of DNA replication and apoptosis.
Conclusion: The study presents evidence that cell sensitization towards cisplatin by sodium butyrate is due to hyperacetylation of histone H4 in specific chromatin regions, which temporarily abrogates the cisplatin imposed cell cycle arrest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate enhances cellular radiosensitivity by inhibiting both DNA nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Sep 5;10(9):970-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Aug 6. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21824827
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors SAHA and sodium butyrate block G1-to-S cell cycle progression in neurosphere formation by adult subventricular cells.BMC Neurosci. 2011 May 26;12:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-50. BMC Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21615950 Free PMC article.
-
Histone proteins determined in a human colon cancer by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2006 Sep 29;1129(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.06.100. Epub 2006 Aug 2. J Chromatogr A. 2006. PMID: 16887128
-
Effects of sodium butyrate, a new pharmacological agent, on cells in culture.Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Feb 5;42(2):65-82. doi: 10.1007/BF00222695. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982. PMID: 6174854 Review.
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity by butyrate.J Nutr. 2003 Jul;133(7 Suppl):2485S-2493S. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.7.2485S. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 12840228 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of sodium butyrate and cisplatin against cervical carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 21;12:999667. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.999667. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36338704 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate suppresses DNA double strand break repair induced by etoposide more effectively in MCF-7 cells than in HEK293 cells.BMC Biochem. 2015 Jan 16;16:2. doi: 10.1186/s12858-014-0030-5. BMC Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25592494 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Apoptosis in Toxoplasma gondii Infected Hela Cells by Cisplatin and Sodium Azide and Isolation of Apoptotic Bodies and Potential Use for Vaccination against Toxoplasma gondii.Iran J Parasitol. 2018 Jul-Sep;13(3):406-415. Iran J Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 30483332 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Human Microbiome in Development and Management of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;17(13):2238. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132238. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium butyrate promotes the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to smooth muscle cells through histone acetylation.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 30;9(12):e116183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116183. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25548915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith KT, Workman J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Anticancer compounds. Int J Biochem & Cell Biol. 2009;41:21–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

