Serum glutamine, set-shifting ability and anorexia nervosa
- PMID: 20576166
- PMCID: PMC2902473
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-859X-9-29
Serum glutamine, set-shifting ability and anorexia nervosa
Abstract
Background: Set-shifting is impaired in people with anorexia nervosa (AN), but the underlying physiological and biochemical processes are unclear. Animal studies have established that glutamatergic pathways in the prefrontal cortex play an important role in set-shifting ability. However, it is not yet understood whether levels of serum glutamatergic amino acids are associated with set-shifting performance in humans. The aim of this study was to determine whether serum concentrations of amino acids related to glutamatergic neurotransmission (glutamine, glutamate, glycine, l-serine, d-serine) are associated with set-shifting ability in people with acute AN and those after recovery.
Methods: Serum concentrations of glutamatergic amino acids were measured in 27 women with current AN (AN group), 18 women recovered from AN (ANRec group) and 28 age-matched healthy controls (HC group). Set-shifting was measured using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) and the Trail Making Task (TMT). Dimensional measures of psychopathology were used, including the Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDEQ), the Maudsley Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory (MOCI) and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS).
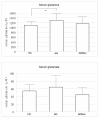
Results: Serum glutamine concentrations in the AN group (1,310.2 +/- 265.6 muM, mean +/- SD) were significantly higher (by approximately 20%) than those in the HC group (1,102.9 +/- 152.7 muM, mean +/- SD) (F(2, 70) = 6.3, P = 0.003, 95% CI 61.2 to 353.4). Concentrations of serum glutamine were positively associated with markers of the illness severity: a negative correlation was present between serum glutamine concentrations and body mass index (BMI) and lowest BMI and a positive correlation was found between duration of illness and EDEQ. The AN group showed significantly impaired set shifting in the WCST, both total errors, and perseverative errors. In the AN group, there were no correlations between serum glutamine concentrations and set shifting.
Conclusions: Serum concentrations of glutamine may be a biomarker of illness severity in people with AN. It does not appear to be directly associated with changes in executive function.
Figures
References
-
- Tchanturia K, Morris R, Anderluh B, Collier D, Nikolaou V, Treasure J. Set shifting in anorexia nervosa: an examination before and after weight gain, in full recovery and relationship to childhood and adult OCPD traits. J Psychiatr Res. 2004;38:545–552. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2004.03.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous