A cascade model connecting life stress to risk behavior among rural African American emerging adults
- PMID: 20576186
- PMCID: PMC2902871
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579410000350
A cascade model connecting life stress to risk behavior among rural African American emerging adults
Abstract
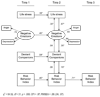
A three-wave cascade model linking life stress to increases in risk behavior was tested with 347 African American emerging adults living in the rural South. Data analyses using structural equation modeling and latent growth curve modeling demonstrated that life stress was linked to increases in risk behavior as African Americans transitioned out of secondary school. The cascade model indicated that life stress fostered increases in negative emotions. Negative emotions, in turn, were linked to increases in affiliations with deviant peers and romantic partners; this forecast increases in risk behavior. The findings supported a stress proliferation framework, in which primary stressors affect increases in secondary stressors that carry forward to influence changes in risk behaviors that can potentially compromise mental health.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Howell CT, McConaughy SH, Stanger C. Six-year predictors of problems in a national sample: IV. Young adult signs of disturbance. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 1998;37:718–727. doi:10.1097/00004583-199807000-00012. - PubMed
-
- Agnew R. Foundation for a general strain theory of crime and delinquency. Criminology. 1992;30:47–87. doi:10.1111/j.1745-9125.1992.tb01093.x.
-
- Allison KR, Adlaf EM, Mates D. Life strain, coping and substance use among high school students. Addiction Research. 1997;5:251–272. doi:10.3109/16066359709005265.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Aquilino WS. From adolescent to young adult: A prospective study of parent-child relations during the transition to adulthood. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 1997;59:670–686. doi:10.2307/353953.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical