Therapeutical use of probiotic formulations in clinical practice
- PMID: 20576332
- PMCID: PMC7172412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clnu.2010.05.004
Therapeutical use of probiotic formulations in clinical practice
Abstract
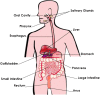
Background & aims: The spreading of gastrointestinal diseases is growing all over the world. Although for some of them an effective therapeutic approach has been found, palliation rather than cure is very frequent due to a partial knowledge of their aetiology and pathogenesis. This review, analyzing the main clinical studies, aims at being a state of the art update of the use of probiotic formulations in daily practice.
Methods: In this review we include all the most significant clinical trials involving the use of probiotic formulations for the treatment of several pathologies.
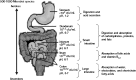
Results: Dysbiosis has been observed in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Probiotics may exert a beneficial effect on Crohn's disease affected patients who have shown gut microbiota antigens and altered wall permeability. Moreover some probiotic formulations seem to enhance the therapy for Helicobacter Pylori reducing its pathogenic potential. Intestinal ecology imbalance has been also linked to cancer induction, allergy, skin and urogenital diseases. In addition probiotics administration seems to be particularly useful to ease post-operative complications.
Conclusion: Further future clinical trials, involving large numbers of patients, will be mandatory to achieve definite evidence of the preventive and curative role of probiotics in medical practice.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd and European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Marchesi Julian, Shanahan Fergus. The normal intestinal microbiota. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20:508–513. - PubMed
-
- Tennyson Christina A., Friedman Gerald. Microecology, obesity, and probiotics. Current opinion in Endocrinology. Diabetes Obes. 2008;15:422–427. - PubMed
-
- Dibaise John K., Zhang Husen, Crowell Michael D., Krajmalnik-Brown Rosa, Anton Decker G., Rittmann Bruce E. Gut microbiota and its possible relationship with obesity. Mayo Clin Proc. April 2008;83(4):460–546. - PubMed
-
- Probiotics. A publication of the institute of food technologists’ expert panel on food safety and nutrition. vol. 53, No. 11 November 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

