Deciphering the kinetic binding mechanism of dimeric ligands using a potent plasma-stable dimeric inhibitor of postsynaptic density protein-95 as an example
- PMID: 20576616
- PMCID: PMC2934690
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.124040
Deciphering the kinetic binding mechanism of dimeric ligands using a potent plasma-stable dimeric inhibitor of postsynaptic density protein-95 as an example
Abstract
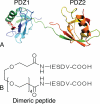
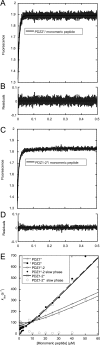
Dimeric ligands can be potent inhibitors of protein-protein or enzyme-substrate interactions. They have increased affinity and specificity toward their targets due to their ability to bind two binding sites simultaneously and are therefore attractive in drug design. However, few studies have addressed the kinetic mechanism of interaction of such bivalent ligands. We have investigated the binding interaction of a recently identified potent plasma-stable dimeric pentapeptide and PDZ1-2 of postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) using protein engineering in combination with fluorescence polarization, isothermal titration calorimetry, and stopped-flow fluorimetry. We demonstrate that binding occurs via a two-step process, where an initial binding to either one of the two PDZ domains is followed by an intramolecular step, which produces the bidentate complex. We have determined all rate constants involved in the binding reaction and found evidence for a conformational transition of the complex. Our data demonstrate the importance of a slow dissociation for a successful dimeric ligand but also highlight the possibility of optimizing the intramolecular association rate. The results may therefore aid the design of dimeric inhibitors in general.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting protein-protein interactions with trimeric ligands: high affinity inhibitors of the MAGUK protein family.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117668. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658767 Free PMC article.
-
Rigidified clicked dimeric ligands for studying the dynamics of the PDZ1-2 supramodule of PSD-95.Chembiochem. 2015 Jan 2;16(1):64-9. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402547. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Chembiochem. 2015. PMID: 25407949
-
A high-affinity, dimeric inhibitor of PSD-95 bivalently interacts with PDZ1-2 and protects against ischemic brain damage.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 28;109(9):3317-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113761109. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22343531 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand binding by PDZ domains.Biofactors. 2012 Sep-Oct;38(5):338-48. doi: 10.1002/biof.1031. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Biofactors. 2012. PMID: 22674855 Review.
-
Streptavidin-binding and -dimerizing ligands discovered by phage display, topochemistry, and structure-based design.Biomol Eng. 1999 Dec 31;16(1-4):57-65. doi: 10.1016/s1050-3862(99)00036-4. Biomol Eng. 1999. PMID: 10796985 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing allosteric inhibition of dihydrodipicolinate synthase through the design and synthesis of novel dimeric compounds.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Jul 25;14(9):1698-1703. doi: 10.1039/d3md00044c. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37731698 Free PMC article.
-
Supertertiary protein structure affects an allosteric network.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 29;117(39):24294-24304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007201117. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32929026 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of multivalent PDZ domain binding to the scaffold protein PSD-95 reveals ternary-complex specificity of combinatorial inhibition.Structure. 2014 Oct 7;22(10):1458-66. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Structure. 2014. PMID: 25220472 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical characterization of the complex between human papillomavirus E6 protein and synapse-associated protein 97.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 4;286(5):3597-606. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.190264. Epub 2010 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21113079 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a PDZbody, a bivalent binder of the E6 protein from human papillomavirus.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 23;5:9382. doi: 10.1038/srep09382. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25797137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mammen M., Choi S. K., Whitesides G. M. (1998) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37, 2754–2794 - PubMed
-
- Clemons P. A. (1999) Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 3, 112–115 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Thomas R. M., Suzuki H., De Brabander J. K., Wang X., Harran P. G. (2004) Science 305, 1471–1474 - PubMed
-
- Long J. F., Tochio H., Wang P., Fan J. S., Sala C., Niethammer M., Sheng M., Zhang M. (2003) J. Mol. Biol. 327, 203–214 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

