Speciation genes in plants
- PMID: 20576737
- PMCID: PMC2924826
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcq126
Speciation genes in plants
Abstract
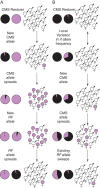
Background: Analyses of speciation genes--genes that contribute to the cessation of gene flow between populations--can offer clues regarding the ecological settings, evolutionary forces and molecular mechanisms that drive the divergence of populations and species. This review discusses the identities and attributes of genes that contribute to reproductive isolation (RI) in plants, compares them with animal speciation genes and investigates what these genes can tell us about speciation.
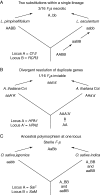
Scope: Forty-one candidate speciation genes were identified in the plant literature. Of these, seven contributed to pre-pollination RI, one to post-pollination, prezygotic RI, eight to hybrid inviability, and 25 to hybrid sterility. Genes, gene families and genetic pathways that were frequently found to underlie the evolution of RI in different plant groups include the anthocyanin pathway and its regulators (pollinator isolation), S RNase-SI genes (unilateral incompatibility), disease resistance genes (hybrid necrosis), chimeric mitochondrial genes (cytoplasmic male sterility), and pentatricopeptide repeat family genes (cytoplasmic male sterility).
Conclusions: The most surprising conclusion from this review is that identities of genes underlying both prezygotic and postzygotic RI are often predictable in a broad sense from the phenotype of the reproductive barrier. Regulatory changes (both cis and trans) dominate the evolution of pre-pollination RI in plants, whereas a mix of regulatory mutations and changes in protein-coding genes underlie intrinsic postzygotic barriers. Also, loss-of-function mutations and copy number variation frequently contribute to RI. Although direct evidence of positive selection on speciation genes is surprisingly scarce in plants, analyses of gene family evolution, along with theoretical considerations, imply an important role for diversifying selection and genetic conflict in the evolution of RI. Unlike in animals, however, most candidate speciation genes in plants exhibit intraspecific polymorphism, consistent with an important role for stochastic forces and/or balancing selection in development of RI in plants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plant speciation.Science. 2007 Aug 17;317(5840):910-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1137729. Science. 2007. PMID: 17702935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The strength of reproductive isolating barriers in seed plants: Insights from studies quantifying premating and postmating reproductive barriers over the past 15 years.Evolution. 2022 Oct;76(10):2228-2243. doi: 10.1111/evo.14565. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Evolution. 2022. PMID: 35838076 Free PMC article.
-
Components of reproductive isolation between Orchis mascula and Orchis pauciflora.Evolution. 2013 Jul;67(7):2083-93. doi: 10.1111/evo.12091. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Evolution. 2013. PMID: 23815661
-
Multiple pre- and postzygotic components of reproductive isolation between two co-occurring Lysimachia species.New Phytol. 2023 Apr;238(2):874-887. doi: 10.1111/nph.18767. Epub 2023 Feb 17. New Phytol. 2023. PMID: 36683441
-
Evolution and Molecular Control of Hybrid Incompatibility in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Aug 11;7:1208. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01208. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27563306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reproductive isolation between populations of Iris atropurpurea is associated with ecological differentiation.Ann Bot. 2016 Oct 1;118(5):971-982. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw139. Ann Bot. 2016. PMID: 27436798 Free PMC article.
-
Clade-Specific Plastid Inheritance Patterns Including Frequent Biparental Inheritance in Passiflora Interspecific Crosses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2278. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052278. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668897 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular evolution and genetics of postzygotic reproductive isolation in plants.F1000 Biol Rep. 2012;4:23. doi: 10.3410/B4-23. Epub 2012 Dec 3. F1000 Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 23236340 Free PMC article.
-
A Genome-Wide Association Study Pinpoints Quantitative Trait Genes for Plant Height, Heading Date, Grain Quality, and Yield in Rye (Secale cereale L.).Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 29;12:718081. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.718081. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34777409 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, putative functionality and interactions between lncRNAs and miRNAs in Brassica species.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 21;8(1):4960. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23334-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29563515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashutosh, Kumar P, Dinesh Kumar V, Sharma PC, Prakash S, Bhat SR. A novel orf108 co-transcribed with the atpA gene is associated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica juncea carrying Moricandia arvensis cytoplasm. Plant & Cell Physiology. 2008;49:284–289. - PubMed

