Orphan nuclear receptors in breast cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic response
- PMID: 20576803
- PMCID: PMC3518023
- DOI: 10.1677/ERC-10-0058
Orphan nuclear receptors in breast cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic response
Abstract
Nuclear receptors comprise a large family of highly conserved transcription factors that regulate many key processes in normal and neoplastic tissues. Most nuclear receptors share a common, highly conserved domain structure that includes a carboxy-terminal ligand-binding domain. However, a subgroup of this gene family is known as the orphan nuclear receptors because to date there are no known natural ligands that regulate their activity. Many of the 25 nuclear receptors classified as orphan play critical roles in embryonic development, metabolism, and the regulation of circadian rhythm. Here, we review the emerging role(s) of orphan nuclear receptors in breast cancer, with a particular focus on two of the estrogen-related receptors (ERRalpha and ERRgamma) and several others implicated in clinical outcome and response or resistance to cytotoxic or endocrine therapies, including the chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factors, nerve growth factor-induced B, DAX-1, liver receptor homolog-1, and retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha. We also propose that a clearer understanding of the function of orphan nuclear receptors in mammary gland development and normal mammary tissues could significantly improve our ability to diagnose, treat, and prevent breast cancer.
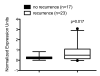
Figures

Similar articles
-
Orphan nuclear receptors as drug targets for the treatment of prostate and breast cancers.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Dec;40(10):1137-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.10.005. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25455729 Review.
-
Minireview: role of orphan nuclear receptors in cancer and potential as drug targets.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Feb;28(2):157-72. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1291. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24295738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An autoregulatory loop controlling orphan nuclear receptor DAX-1 gene expression by orphan nuclear receptor ERRgamma.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Nov 28;33(21):6756-68. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki976. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. Retraction in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Feb 20;47(3):1604. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1272. PMID: 16314306 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The ROR nuclear orphan receptor subfamily: critical regulators of multiple biological processes.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;69:205-47. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)69048-2. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11550795 Review.
-
Estrogen-related receptors alpha, beta and gamma expression and function is associated with transcriptional repressor EZH2 in breast carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jun 26;18(1):690. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4586-0. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29940916 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Research resource: nuclear receptors as transcriptome: discriminant and prognostic value in breast cancer.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Feb;27(2):350-65. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1265. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23292282 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan Nuclear Receptors in Colorectal Cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2018 Oct;24(4):815-819. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0440-6. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Pathol Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 29956064 Review.
-
ERRγ target genes are poor prognostic factors in Tamoxifen-treated breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015 May 15;34(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0150-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25971350 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Receptor 4A2 (NR4A2/NURR1) Regulates Autophagy and Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2021 Nov;1(2):65-78. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.crc-21-0073. Cancer Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 35582016 Free PMC article.
-
NR2F6, a new immune checkpoint that acts as a potential biomarker of immunosuppression and contributes to poor clinical outcome in human glioma.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 28;14:1139268. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1139268. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37575237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akli S, Zheng P, Multani A, Wingate H, Pathak S, Zhang N, Tucker S, Chang S, Keyomarsi K. Tumor-specific low molecular weight forms of cyclin E induce genomic instability and resistance to p21, p27, and antiestrogens in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3198–3208. - PubMed
-
- Allred D, Medina D. The relevance of mouse models to understanding the development and progression of human breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008;13:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Ariazi EA, Clark GM, Mertz JE. Estrogen-related receptor alpha and estrogen-related receptor gamma associate with unfavorable and favorable biomarkers, respectively, in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6510–6518. - PubMed
-
- Ariazi EA, Jordan VC. Estrogen-related receptors as emerging targets in cancer and metabolic disorders. Curr.Top.Med.Chem. 2006;6:203–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

