TGF-beta receptor deletion in the renal collecting system exacerbates fibrosis
- PMID: 20576806
- PMCID: PMC2938601
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010020147
TGF-beta receptor deletion in the renal collecting system exacerbates fibrosis
Abstract
TGF-beta plays a key role in upregulating matrix production in injury-induced renal fibrosis, but how TGF-beta signaling in distinct compartments of the kidney, such as specific segments of the nephron, affects the response to injury is unknown. In this study, we determined the role of TGF-beta signaling both in development of the renal collecting system and in response to injury by selectively deleting the TGF-beta type II receptor in mice at the initiation of ureteric bud development. These mice developed normally but demonstrated a paradoxic increase in fibrosis associated with enhanced levels of active TGF-beta after unilateral ureteral obstruction. Consistent with this observation, TGF-beta type II receptor deletion in cultured collecting duct cells resulted in excessive integrin alphavbeta6-dependent TGF-beta activation that increased collagen synthesis in co-cultured renal interstitial fibroblasts. These results suggest that inhibiting TGF-beta receptor-mediated function in collecting ducts may exacerbate renal fibrosis by enhancing paracrine TGF-beta signaling between epithelial and interstitial cells.
Figures
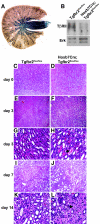
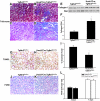
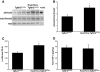
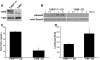
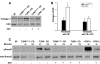
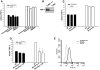
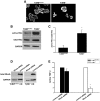
Comment in
-
TGF-beta signaling and the renal tubular epithelial cell: too much, too little, and just right.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Aug;21(8):1241-3. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010060676. Epub 2010 Jul 22. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20651160 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Renal fibrosis is not reduced by blocking transforming growth factor-β signaling in matrix-producing interstitial cells.Kidney Int. 2015 Sep;88(3):503-14. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.51. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25760325 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of β1-integrin in collecting duct principal cells leads to tubular injury and renal medullary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Oct 1;313(4):F1026-F1037. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00038.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28701310 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse roles of TGF-β receptor II in renal fibrosis and inflammation in vivo and in vitro.J Pathol. 2012 Jun;227(2):175-88. doi: 10.1002/path.3976. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22190171
-
Curtailing endothelial TGF-β signaling is sufficient to reduce endothelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis in CKD.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Apr;26(4):817-29. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013101137. Epub 2014 Dec 22. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25535303 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Mar;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-3. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-245MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 25830829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How does TGF-β mediate tubulointerstitial fibrosis?Semin Nephrol. 2012 May;32(3):228-35. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.04.001. Semin Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22835453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal fibrosis is not reduced by blocking transforming growth factor-β signaling in matrix-producing interstitial cells.Kidney Int. 2015 Sep;88(3):503-14. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.51. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 25760325 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing actions of renal tubular- and myeloid-derived porcupine in obstruction-induced kidney fibrosis.Kidney Int. 2019 Dec;96(6):1308-1319. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.06.020. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 31585741 Free PMC article.
-
Tubular β-catenin and FoxO3 interactions protect in chronic kidney disease.JCI Insight. 2020 May 21;5(10):e135454. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135454. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32369448 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum protein TXNDC5 promotes renal fibrosis by enforcing TGF-β signaling in kidney fibroblasts.J Clin Invest. 2021 Mar 1;131(5):e143645. doi: 10.1172/JCI143645. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33465051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M, Wang XF, Massague J: TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell 71: 1003–1014, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Yamashita H, ten Dijke P, Franzen P, Miyazono K, Heldin CH: Formation of hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II receptors for transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem 269: 20172–20178, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Roberts AB, Tian F, Byfield SD, Stuelten C, Ooshima A, Saika S, Flanders KC: Smad3 is key to TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis, tumor suppression and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17: 19–27, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB: Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci 116: 217–224, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Daniel C, Wiede J, Krutzsch HC, Ribeiro SM, Roberts DD, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Hugo C: Thrombospondin-1 is a major activator of TGF-beta in fibrotic renal disease in the rat in vivo. Kidney Int 65: 459–468, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

