Small molecule disruption of G beta gamma signaling inhibits the progression of heart failure
- PMID: 20576935
- PMCID: PMC2924955
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.217075
Small molecule disruption of G beta gamma signaling inhibits the progression of heart failure
Abstract
Rationale: Excess signaling through cardiac Gbetagamma subunits is an important component of heart failure (HF) pathophysiology. They recruit elevated levels of cytosolic G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK)2 to agonist-stimulated beta-adrenergic receptors (beta-ARs) in HF, leading to chronic beta-AR desensitization and downregulation; these events are all hallmarks of HF. Previous data suggested that inhibiting Gbetagamma signaling and its interaction with GRK2 could be of therapeutic value in HF.
Objective: We sought to investigate small molecule Gbetagamma inhibition in HF.
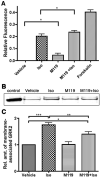
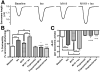
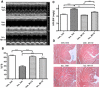
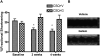
Methods and results: We recently described novel small molecule Gbetagamma inhibitors that selectively block Gbetagamma-binding interactions, including M119 and its highly related analog, gallein. These compounds blocked interaction of Gbetagamma and GRK2 in vitro and in HL60 cells. Here, we show they reduced beta-AR-mediated membrane recruitment of GRK2 in isolated adult mouse cardiomyocytes. Furthermore, M119 enhanced both adenylyl cyclase activity and cardiomyocyte contractility in response to beta-AR agonist. To evaluate their cardiac-specific effects in vivo, we initially used an acute pharmacological HF model (30 mg/kg per day isoproterenol, 7 days). Concurrent daily injections prevented HF and partially normalized cardiac morphology and GRK2 expression in this acute HF model. To investigate possible efficacy in halting progression of preexisting HF, calsequestrin cardiac transgenic mice (CSQ) with extant HF received daily injections for 28 days. The compound alone halted HF progression and partially normalized heart size, morphology, and cardiac expression of HF marker genes (GRK2, atrial natriuretic factor, and beta-myosin heavy chain).
Conclusions: These data suggest a promising therapeutic role for small molecule inhibition of pathological Gbetagamma signaling in the treatment of HF.
Figures
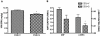
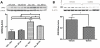
References
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, Jessup M, Konstam MA, Mancini DM, Michl K, Oates JA, Rahko PS, Silver MA, Stevenson LW, Yancy CW, Antman EM, Smith SC, Jr., Adams CD, Anderson JL, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Halperin JL, Hiratzka LF, Jacobs AK, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B. ACC/AHA 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Update the 2001 Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Heart Failure): developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians and the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2005;112:e154–235. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O’Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2009 Update. A Report From the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Pitcher JA, Inglese J, Higgins JB, Arriza JL, Casey PJ, Kim C, Benovic JL, Kwatra MM, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science. 1992;257:1264–1267. - PubMed
-
- Bristow MR, Ginsburg R, Minobe W, Cubicciotti RS, Sageman WS, Lurie K, Billingham ME, Harrison DC, Stinson EB. Decreased catecholamine sensitivity and beta-adrenergic-receptor density in failing human hearts. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Ungerer M, Bohm M, Elce JS, Erdmann E, Lohse MJ. Altered expression of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and beta 1-adrenergic receptors in the failing human heart. Circulation. 1993;87:454–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

