Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state
- PMID: 20577053
- PMCID: PMC2898585
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI40671
Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state
Abstract
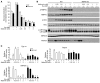
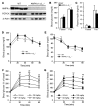
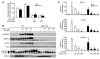
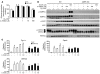
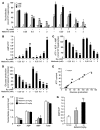
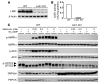
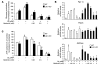
Metformin is widely used to treat hyperglycemia in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Recently the LKB1/AMP-activated protein kinase (LKB1/AMPK) pathway was proposed to mediate the action of metformin on hepatic gluconeogenesis. However, the molecular mechanism by which this pathway operates had remained elusive. Surprisingly, here we have found that in mice lacking AMPK in the liver, blood glucose levels were comparable to those in wild-type mice, and the hypoglycemic effect of metformin was maintained. Hepatocytes lacking AMPK displayed normal glucose production and gluconeogenic gene expression compared with wild-type hepatocytes. In contrast, gluconeogenesis was upregulated in LKB1-deficient hepatocytes. Metformin decreased expression of the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), while cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pepck) gene expression was unaffected in wild-type, AMPK-deficient, and LKB1-deficient hepatocytes. Surprisingly, metformin-induced inhibition of glucose production was amplified in both AMPK- and LKB1-deficient compared with wild-type hepatocytes. This inhibition correlated in a dose-dependent manner with a reduction in intracellular ATP content, which is crucial for glucose production. Moreover, metformin-induced inhibition of glucose production was preserved under forced expression of gluconeogenic genes through PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) overexpression, indicating that metformin suppresses gluconeogenesis via a transcription-independent process. In conclusion, we demonstrate that metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in an LKB1- and AMPK-independent manner via a decrease in hepatic energy state.
Figures
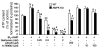
Comment in
-
An energetic tale of AMPK-independent effects of metformin.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jul;120(7):2267-70. doi: 10.1172/JCI43661. Epub 2010 Jun 23. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20577046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

