Mitigation of hematologic radiation toxicity in mice through pharmacological quiescence induced by CDK4/6 inhibition
- PMID: 20577054
- PMCID: PMC2898594
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI41402
Mitigation of hematologic radiation toxicity in mice through pharmacological quiescence induced by CDK4/6 inhibition
Abstract
Total body irradiation (TBI) can induce lethal myelosuppression, due to the sensitivity of proliferating hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) to ionizing radiation (IR). No effective therapy exists to mitigate the hematologic toxicities of TBI. Here, using selective and structurally distinct small molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and CDK6, we have demonstrated that selective cellular quiescence increases radioresistance of human cell lines in vitro and mice in vivo. Cell lines dependent on CDK4/6 were resistant to IR and other DNA-damaging agents when treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors. In contrast, CDK4/6 inhibitors did not protect cell lines that proliferated independently of CDK4/6 activity. Treatment of wild-type mice with CDK4/6 inhibitors induced reversible pharmacological quiescence (PQ) of early HSPCs but not most other cycling cells in the bone marrow or other tissues. Selective PQ of HSPCs decreased the hematopoietic toxicity of TBI, even when the CDK4/6 inhibitor was administered several hours after TBI. Moreover, PQ at the time of administration of therapeutic IR to mice harboring autochthonous cancers reduced treatment toxicity without compromising the therapeutic tumor response. These results demonstrate an effective method to mitigate the hematopoietic toxicity of IR in mammals, which may be potentially useful after radiological disaster or as an adjuvant to anticancer therapy.
Figures
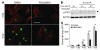
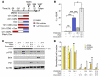
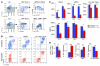
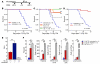

Comment in
-
Radioprotection: smart games with death.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jul;120(7):2270-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI43794. Epub 2010 Jun 23. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20577043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elkind MM, Sutton H. X-ray damage and recovery in mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1959;184:1293–1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008581/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- GM008581/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080421/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG034806/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI077454/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI080432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA086860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG024379/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F30-AG034806/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122023/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI077454/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM008719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

