Systemic inflammation and liver injury following hemorrhagic shock and peripheral tissue trauma involve functional TLR9 signaling on bone marrow-derived cells and parenchymal cells
- PMID: 20577143
- PMCID: PMC3000874
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181eddcab
Systemic inflammation and liver injury following hemorrhagic shock and peripheral tissue trauma involve functional TLR9 signaling on bone marrow-derived cells and parenchymal cells
Abstract
Hemorrhagic shock due to trauma (HS/T) induces an inflammatory response that can contribute to end-organ injury. The pathways involved in the initiation and propagation of HS/T-induced inflammation are incompletely understood. Here, we hypothesized that the DNA sensor TLR9 would have a role in inflammatory signaling after HS/T. Using mice expressing a nonfunctional, mutant form of TLR9, we identified a role of TLR9 in driving the initial cytokine response and liver damage in a model of hemorrhagic shock and bilateral femur fracture. Circulating DNA levels were found to correlate with the degree of tissue damage. Experiments using chimeric mice show that TLR9 on both bone marrow-derived cells and parenchymal cells are important for the TLR9-mediated liver and tissue damage, as well as systemic inflammation after HS/T. These data suggest that release of DNA may be a driver of the inflammatory response to severe injury as well as a marker of the extent of tissue damage. One of the sensors of DNA in the setting of HS/T seems to be TLR9.
Figures
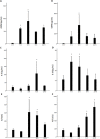
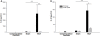
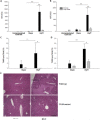
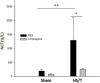
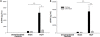
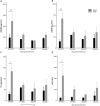
References
-
- Dewar D, Moore FA, Moore EE, Balogh Z. Postinjury multiple organ failure. Injury. 2009;40:912–918. - PubMed
-
- Lenz A, Franklin GA, Cheadle WG. Systemic inflammation after trauma. Injury. 2007;38:1336–1345. - PubMed
-
- Faist E, Baue AE, Dittmer H, Heberer G. Multiple organ failure in polytrauma patients. J Trauma. 1983;23:775–787. - PubMed
-
- Strecker W, Gebhard F, Rager J, Bruckner UB, Steinbach G, Kinzl L. Early biochemical characterization of soft-tissue trauma and fracture trauma. J Trauma. 1999;47:358–364. - PubMed
-
- Moore EE. Synergy of bone fractures, soft tissue disruption, and hemorrhagic shock in the genesis of postinjury immunochaos: the pathway to multiple organ failure. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:1305–1306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

