Sepsis-induced alterations in protein-protein interactions within mTOR complex 1 and the modulating effect of leucine on muscle protein synthesis
- PMID: 20577146
- PMCID: PMC2995824
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181ecb57c
Sepsis-induced alterations in protein-protein interactions within mTOR complex 1 and the modulating effect of leucine on muscle protein synthesis
Abstract
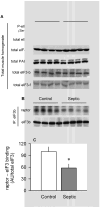
Sepsis-induced muscle atrophy is produced in part by decreased protein synthesis mediated by inhibition of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). The present study tests the hypothesis that alteration of specific protein-protein interactions within the mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1) contributes to the decreased mTOR activity observed after cecal ligation and puncture in rats. Sepsis decreased in vivo translational efficiency in gastrocnemius and reduced the phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4E-binding protein (BP) 1, S6 kinase (S6K) 1, and mTOR, compared with time-matched pair-fed controls. Sepsis decreased T246-phosphorylated PRAS40 (proline-rich Akt substrate 40) and reciprocally increased S792-phosphorylated raptor (regulatory associated protein of mTOR). Despite these phosphorylation changes, sepsis did not alter PRAS40 binding to raptor. The amount of the mTOR-raptor complex did not differ between groups. In contrast, the binding and retention of both 4E-BP1 and S6K1 to raptor were increased, and, conversely, the binding of raptor with eIF3 was decreased in sepsis. These changes in mTORC1 in the basal state were associated with enhanced 5'-AMP activated kinase activity. Acute in vivo leucine stimulation increased muscle protein synthesis in control, but not septic rats. This muscle leucine resistance was associated with coordinated changes in raptor-eIF3 binding and 4E-BP1 phosphorylation. Overall, our data suggest the sepsis-induced decrease in muscle protein synthesis may be mediated by the inability of 4E-BP1 and S6K1 to be phosphorylated and released from mTORC1 as well as the decreased recruitment of eIF3 necessary for a functional 48S complex. These data provide additional mechanistic insight into the molecular mechanisms by which sepsis impairs both basal protein synthesis and the anabolic response to the nutrient signal leucine in skeletal muscle.
Figures









References
-
- Long CL, Jeevanandam M, Kim BM, Kinney JM. Whole body protein synthesis and catabolism in septic man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977;30:1340–1344. - PubMed
-
- Lang CH, Frost RA. Sepsis-induced suppression of skeletal muscle translation initiation mediated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Metabolism. 2007;56:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Lang CH, Frost RA, Vary TC. Regulation of muscle protein synthesis during sepsis and inflammation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293:E453–E459. - PubMed
-
- Hinton TM, Coldwell MJ, Carpenter GA, Morley SJ, Pain VM. Functional analysis of individual binding activities of the scaffold protein eIF4G. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:1695–1708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

