Activation of autophagy during cell death requires the engulfment receptor Draper
- PMID: 20577216
- PMCID: PMC2892814
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09127
Activation of autophagy during cell death requires the engulfment receptor Draper
Abstract
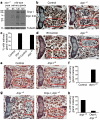
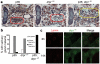
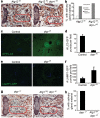
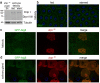
Autophagy degrades cytoplasmic components that are required for cell survival in response to starvation. Autophagy has also been associated with cell death, but it is unclear how this is distinguished from autophagy during cell survival. Drosophila salivary glands undergo programmed cell death that requires autophagy genes, and engulfment of salivary gland cells by phagocytes does not appear to occur. Here we show that Draper (Drpr), the Drosophila melanogaster orthologue of the Caenorhabditis elegans engulfment receptor CED-1, is required for autophagy during cell death. Null mutations in, and salivary gland-specific knockdown of, drpr inhibit salivary gland degradation. Knockdown of drpr prevents the induction of autophagy in dying salivary glands, and expression of the Atg1 autophagy regulator in drpr mutants suppresses the failure in degradation of salivary glands. Surprisingly, drpr is required in the same dying salivary gland cells in which it regulates autophagy induction, but drpr knockdown does not prevent starvation-induced autophagy in the fat body, which is associated with survival. In addition, components of the conserved engulfment pathway are required for clearance of dying salivary glands. To our knowledge, this is the first example of an engulfment factor that is required for self-clearance of cells. Further, Drpr is the first factor that distinguishes autophagy that is associated with cell death from autophagy associated with cell survival.
Figures
References
-
- Pandey UB, et al. HDAC6 rescues neurodegeneration and provides an essential link between autophagy and the UPS. Nature. 2007;447:859. - PubMed
-
- Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM. Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development. 1994;120:2121. - PubMed
-
- Rusten TE, et al. Programmed autophagy in the Drosophila fat body is induced by ecdysone through regulation of the PI3K pathway. Dev. Cell. 2004;7:179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

