Enhanced Delivery of Erythropoietin Across the Blood-Brain Barrier for Neuroprotection against Ischemic Neuronal Injury
- PMID: 20577577
- PMCID: PMC2888513
- DOI: 10.1007/s12975-010-0019-3
Enhanced Delivery of Erythropoietin Across the Blood-Brain Barrier for Neuroprotection against Ischemic Neuronal Injury
Abstract
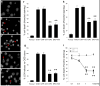
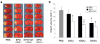
Due to limited penetration of the BBB, many therapeutic agents in clinical use require higher doses in order to reach effective concentrations in brain. In some instances, these high doses elicit severe side effects. In the case of erythropoietin (EPO), an established neuroprotectant against ischemic brain injury, its low BBB permeability requires such a high therapeutic dose that it can induce dangerous complications such as polycythmia and secondary stroke. The purpose of this study is to generate a modified EPO that has increased facility crossing the BBB without losing its neuroprotective element. We have engineered a fusion protein (EPO-TAT) by tagging a protein transduction domain derived from HIV TAT to the EPO protein. This sequence enhanced the capacity of EPO to cross the BBB in animals at least twofold when IP administered and up to five-fold when IV administered. In vitro experiments showed that this EPO fusion protein retained all its protective properties against neuronal death elicited by oxygen-glucose deprivation and NMDA insults. The needed therapeutic dose of the EPO-TAT was decreased by ~10-fold compared to that of regular EPO to achieve equivalent neuroprotection in terms of reducing volume of infarction induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Our results support the approach of using a protein transduction domain coupled to therapeutic agents. In this way, not only can the therapeutic doses be lowered, but agents without BBB permeability may now be available for clinical applications.
Figures
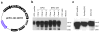

Similar articles
-
The neuroprotective mechanism of erythropoietin-TAT fusion protein against neurodegeneration from ischemic brain injury.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(8):1465-74. doi: 10.2174/1871527313666140806155259. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25106625
-
Neuroprotection in stroke in the mouse with intravenous erythropoietin-Trojan horse fusion protein.Brain Res. 2011 Jan 19;1369:203-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.097. Epub 2010 Oct 31. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21047502
-
Neuroprotection in experimental stroke in the rat with an IgG-erythropoietin fusion protein.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 11;1360:193-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.009. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20833153
-
The nasal route as a potential pathway for delivery of erythropoietin in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in humans.ScientificWorldJournal. 2009 Sep 15;9:970-81. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2009.103. ScientificWorldJournal. 2009. PMID: 19768354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin and derivatives: Potential beneficial effects on the brain.J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(5):1032-1057. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15475. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34278579 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Penetrating Bifunctional Erythropoietin-Transferrin Receptor Antibody Fusion Protein for Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Pharm. 2018 Nov 5;15(11):4963-4973. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00594. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30252487 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Neuroprotective Erythropoietin Modified with a Novel Carrier for the Blood-Brain Barrier.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):1184-1196. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00845-2. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32144722 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal injection of recombinant human erythropoietin improves cognitive and visual impairments in chronic cerebral ischemia rats.Biomed Rep. 2020 Nov;13(5):40. doi: 10.3892/br.2020.1347. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Biomed Rep. 2020. PMID: 32934813 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant erythropoietin without erythropoietic activity is neuroprotective against ischemic brain injury.Stroke. 2012 Nov;43(11):3071-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.663120. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22984011 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Erythropoietin Protects CA1 Hippocampal Cells, Modulated by Specific Time Pattern Molecular Changes After Ischemic Damage in Rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Aug;68(4):590-602. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01308-w. Epub 2019 May 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31054091
References
-
- Brines M, Cerami A. Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005 Jun;6(6):484–94. - PubMed
-
- Wiessner C, Allegrini PR, Ekatodramis D, Jewell UR, Stallmach T, Gassmann M. Increased cerebral infarct volumes in polyglobulic mice overexpressing erythropoietin. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001 Jul;21(7):857–64. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

