Reading as active sensing: a computational model of gaze planning in word recognition
- PMID: 20577589
- PMCID: PMC2889689
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2010.00006
Reading as active sensing: a computational model of gaze planning in word recognition
Abstract
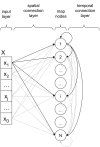
WE OFFER A COMPUTATIONAL MODEL OF GAZE PLANNING DURING READING THAT CONSISTS OF TWO MAIN COMPONENTS: a lexical representation network, acquiring lexical representations from input texts (a subset of the Italian CHILDES database), and a gaze planner, designed to recognize written words by mapping strings of characters onto lexical representations. The model implements an active sensing strategy that selects which characters of the input string are to be fixated, depending on the predictions dynamically made by the lexical representation network. We analyze the developmental trajectory of the system in performing the word recognition task as a function of both increasing lexical competence, and correspondingly increasing lexical prediction ability. We conclude by discussing how our approach can be scaled up in the context of an active sensing strategy applied to a robotic setting.
Keywords: SOM; active sensing; lexical representation network; prediction; reading; serial order encoding.
Figures





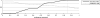
Similar articles
-
How strongly do word reading times and lexical decision times correlate? Combining data from eye movement corpora and megastudies.Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2013;66(3):563-80. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.658820. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2013. PMID: 22524868
-
From orthography to phonetics: ERP measures of grapheme-to-phoneme conversion mechanisms in reading.J Cogn Neurosci. 2004 Mar;16(2):301-17. doi: 10.1162/089892904322984580. J Cogn Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15068599 Clinical Trial.
-
Lexical is as lexical does: computational approaches to lexical representation.Lang Cogn Neurosci. 2015 Apr 21;30(4):395-408. doi: 10.1080/23273798.2015.1005637. Lang Cogn Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25893204 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic impairment with and without surface dyslexia: Implications for models of reading.Cogn Neuropsychol. 2005 Sep;22(6):695-717. doi: 10.1080/02643290442000257. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2005. PMID: 21038273
-
Parafoveal preview benefit is modulated by the precision of skilled readers' lexical representations.J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2015 Feb;41(1):219-32. doi: 10.1037/xhp0000017. Epub 2014 Nov 10. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform. 2015. PMID: 25384238
Cited by
-
Embodiment and Schizophrenia: A Review of Implications and Applications.Schizophr Bull. 2017 Jul 1;43(4):745-753. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbw220. Schizophr Bull. 2017. PMID: 28338892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Active Inference and Scene Construction.Front Artif Intell. 2020 Oct 28;3:509354. doi: 10.3389/frai.2020.509354. eCollection 2020. Front Artif Intell. 2020. PMID: 33733195 Free PMC article.
-
Generative models, linguistic communication and active inference.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Nov;118:42-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 32687883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep temporal models and active inference.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Jul;90:486-501. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 May 8. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 29747865 Free PMC article.
-
Deep temporal models and active inference.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 Jun;77:388-402. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017. PMID: 28416414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baayen H. (2007). “Storage and computation in the mental lexicon,” In The Mental Lexicon: Core Perspectives, eds Jarema G., Libben G. (Amsterdam: Elsevier; ), 81–104
-
- Baddeley A. D. (1964). Immediate memory and the “perception” of letter sequences. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 16, 364–36710.1080/17470216408416394 - DOI
-
- Baddeley A. D. (2007). Working Memory, Thought, and Action Oxford: Oxford University Press
-
- Ballard D. H. (1991). Animate vision. Artif. Intell. 48, 1–2710.1016/0004-3702(91)90080-4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

