Three-dimensional diffusion tensor microimaging for anatomical characterization of the mouse brain
- PMID: 20577980
- PMCID: PMC2915547
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22426
Three-dimensional diffusion tensor microimaging for anatomical characterization of the mouse brain
Abstract
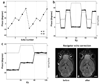
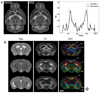
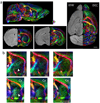
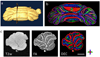
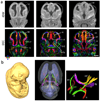
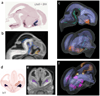
Diffusion tensor imaging is gaining increasing importance for anatomical imaging of the developing mouse brain. However, the application of diffusion tensor imaging to mouse brain imaging at microscopic levels is hindered by the limitation on achievable spatial resolution. In this study, fast diffusion tensor microimaging of the mouse brain, based on a diffusion-weighted gradient and spin echo technique with twin-navigator echo phase correction, is presented. Compared to echo planar and spin echo acquisition, the diffusion-weighted gradient and spin echo acquisition resulted in significant reduction in scan time and had minimal image distortion, thereby allowing acquisition at higher spatial resolution. In this study, three-dimensional diffusion tensor microimaging of the mouse brains at spatial resolutions of 50-60 microm revealed unprecedented anatomical details. Thin fiber bundles in the adult striatum and white matter tracts in the embryonic day 12 mouse brains were visualized for the first time. The study demonstrated that data acquired using the diffusion tensor microimaging technique allow three-dimensional mapping of gene expression data and can serve as a platform to study gene expression patterns in the context of neuroanatomy in the developing mouse brain.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Sunkin SM. Towards the integration of spatially and temporally resolved murine gene expression databases. Trends in Genetics. 2006;22(4):211–217. - PubMed
-
- Paxinos G, Halliday GH, Watson C, Koutcherov Y, Wang H. Atlas of the Developing Mouse Brain at E17.5, P0 and P6. Academic Press; 2006.
-
- Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ, Chen L, Chen TM, Chin MC, Chong J, Crook BE, Czaplinska A, Dang CN, Datta S, Dee NR, Desaki AL, Desta T, Diep E, Dolbeare TA, Donelan MJ, Dong HW, Dougherty JG, Duncan BJ, Ebbert AJ, Eichele G, Estin LK, Faber C, Facer BA, Fields R, Fischer SR, Fliss TP, Frensley C, Gates SN, Glattfelder KJ, Halverson KR, Hart MR, Hohmann JG, Howell MP, Jeung DP, Johnson RA, Karr PT, Kawal R, Kidney JM, Knapik RH, Kuan CL, Lake JH, Laramee AR, Larsen KD, Lau C, Lemon TA, Liang AJ, Liu Y, Luong LT, Michaels J, Morgan JJ, Morgan RJ, Mortrud MT, Mosqueda NF, Ng LL, Ng R, Orta GJ, Overly CC, Pak TH, Parry SE, Pathak SD, Pearson OC, Puchalski RB, Riley ZL, Rockett HR, Rowland SA, Royall JJ, Ruiz MJ, Sarno NR, Schaffnit K, Shapovalova NV, Sivisay T, Slaughterbeck CR, Smith SC, Smith KA, Smith BI, Sodt AJ, Stewart NN, Stumpf KR, Sunkin SM, Sutram M, Tam A, Teemer CD, Thaller C, Thompson CL, Varnam LR, Visel A, Whitlock RM, Wohnoutka PE, Wolkey CK, Wong VY, Wood M, Yaylaoglu MB, Young RC, Youngstrom BL, Yuan XF, Zhang B, Zwingman TA, Jones AR. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature. 2007;445(7124):168–176. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe J, Ahlgren U, Perry P, Hill B, Ross A, Hecksher-Sorensen J, Baldock R, Davidson D. Optical projection tomography as a tool for 3D microscopy and gene expression studies. Science. 2002;296(5567):541–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

