Regulation of the G2/M transition in rodent oocytes
- PMID: 20578061
- PMCID: PMC3995478
- DOI: 10.1002/mrd.21175
Regulation of the G2/M transition in rodent oocytes
Abstract
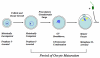
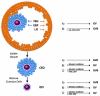
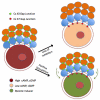
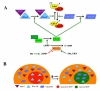
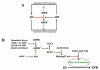
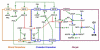
Regulation of maturation in meiotically competent mammalian oocytes is a complex process involving the carefully coordinated exchange of signals between the somatic and germ cell compartments of the ovarian follicle via paracrine and cell-cell coupling pathways. This review highlights recent advances in our understanding of how such signaling controls both meiotic arrest and gonadotropin-triggered meiotic resumption in competent oocytes and relates them to the historical context. Emphasis will be on rodent systems, where many of these new findings have taken place. A regulatory scheme is then proposed that integrates this information into an overall framework for meiotic regulation that demonstrates the complex interplay between different follicular compartments.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Albertini DF, Combelles CMH, Benecci E, Carabatsos MJ. Cellular basis for paracrine regulation of ovarian follicle development. Reproduction. 2001;121:647–653. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD98059 is a specific inhibitor of activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Naito K, Haraguchi S, Suzuki R, Yokoyama M, Inoue M, Aizawa S, Toyoda Y, Sato E. Meiotic abnormalities of c-MOS knockout mouse oocytes: Activation after first meiosis or entrance into third meiotic metaphase. Biol Reprod. 1996;55:1315–1324. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi H, Cao X, Motola S, Popliker M, Conti M, Tsafriri A. Epidermal growth factor family members: mediators of the ovulatory response. Endocrinology. 2005;146:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ami I, Freimann S, Armon L, Dantes A, Ron-El R, Amsterdam A. Novel function of ovarian growth factors: combined studies by DNA microarray, biochemical and physiological approaches. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006;12:413–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

