Manifold modeling for brain population analysis
- PMID: 20579930
- PMCID: PMC3020141
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2010.05.008
Manifold modeling for brain population analysis
Abstract
This paper describes a method for building efficient representations of large sets of brain images. Our hypothesis is that the space spanned by a set of brain images can be captured, to a close approximation, by a low-dimensional, nonlinear manifold. This paper presents a method to learn such a low-dimensional manifold from a given data set. The manifold model is generative-brain images can be constructed from a relatively small set of parameters, and new brain images can be projected onto the manifold. This allows to quantify the geometric accuracy of the manifold approximation in terms of projection distance. The manifold coordinates induce a Euclidean coordinate system on the population data that can be used to perform statistical analysis of the population. We evaluate the proposed method on the OASIS and ADNI brain databases of head MR images in two ways. First, the geometric fit of the method is qualitatively and quantitatively evaluated. Second, the ability of the brain manifold model to explain clinical measures is analyzed by linear regression in the manifold coordinate space. The regression models show that the manifold model is a statistically significant descriptor of clinical parameters.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




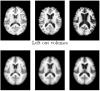

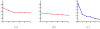



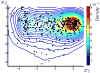

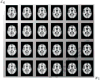
References
-
- Lorenzen P, Davis BC, Joshi S. Unbiased atlas formation via large deformations metric mapping. MICCAI. 2005:411–418. - PubMed
-
- Joshi S, Davis B, Jomier M, Gerig G. Unbiased diffeomorphic atlas construction for computational anatomy. NeuroImage. 2004;23(Supplement 1):S151–S160. mathematics in Brain Imaging. - PubMed
-
- Avants B, Gee JC. Geodesic estimation for large deformation anatomical shape averaging and interpolation. NeuroImage. 2004;23(Supplement 1):S139–S150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG05681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01EB007688-02/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021910/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH071616/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB007688/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB005149/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54-EB005149/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG03991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

