Nesfatin-1--role as possible new potent regulator of food intake
- PMID: 20580651
- PMCID: PMC2902658
- DOI: 10.1016/j.regpep.2010.05.002
Nesfatin-1--role as possible new potent regulator of food intake
Abstract
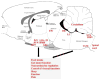
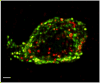
Nesfatin-1 is an 82 amino acid peptide recently discovered in the brain which is derived from nucleobindin2 (NUCB2), a protein that is highly conserved across mammalian species. Nesfatin-1 has received much attention over the past two years due to its reproducible food intake-reducing effect that is linked with recruitment of other hypothalamic peptides regulating feeding behavior. A growing amount of evidence also supports that various stressors activate fore- and hindbrain NUCB2/nesfatin-1 circuitries. In this review, we outline the central nervous system distribution of NUCB2/nesfatin-1, and recent developments on the peripheral expression of NUCB2/nesfatin-1, in particular its co-localization with ghrelin in gastric X/A-like cells and insulin in ss-cells of the endocrine pancreas. Functional studies related to the characteristics of nesfatin-1's inhibitory effects on dark phase food intake are detailed as well as the central activation of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 immunopositive neurons in the response to psychological, immune and visceral stressors. Lastly, potential clinical implications of targeting NUCB2/nesfatin-1 signaling and existing gaps in knowledge to ascertain the role and mechanisms of action of nesfatin-1 are presented.
Figures
References
-
- Oh-I S, Shimizu H, Satoh T, Okada S, Adachi S, Inoue K, Eguchi H, Yamamoto M, Imaki T, Hashimoto K, Tsuchiya T, Monden T, Horiguchi K, Yamada M, Mori M. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2006;443:709–12. - PubMed
-
- Brailoiu GC, Dun SL, Brailoiu E, Inan S, Yang J, Chang JK, Dun NJ. Nesfatin-1: distribution and interaction with a G protein-coupled receptor in the rat brain. Endocrinology. 2007;148:5088–94. - PubMed
-
- Foo K, Brismar H, Broberger C. Distribution and neuropeptide coexistence of nucleobindin-2 mRNA/nesfatin-like immunoreactivity in the rat CNS. Neuroscience. 2008;156:563–79. - PubMed
-
- Fort P, Salvert D, Hanriot L, Jego S, Shimizu H, Hashimoto K, Mori M, Luppi PH. The satiety molecule nesfatin-1 is co-expressed with melanin concentrating hormone in tuberal hypothalamic neurons of the rat. Neuroscience. 2008;155:174–81. - PubMed
-
- Kohno D, Nakata M, Maejima Y, Shimizu H, Sedbazar U, Yoshida N, Dezaki K, Onaka T, Mori M, Yada T. Nesfatin-1 neurons in paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat hypothalamus coexpress oxytocin and vasopressin and are activated by refeeding. Endocrinology. 2008;149:1295–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

