Inhibition of bacterial growth and intramniotic infection in a guinea pig model of chorioamnionitis using PAMAM dendrimers
- PMID: 20580797
- PMCID: PMC2908334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.05.030
Inhibition of bacterial growth and intramniotic infection in a guinea pig model of chorioamnionitis using PAMAM dendrimers
Abstract
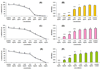
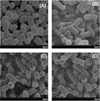
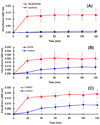
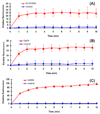
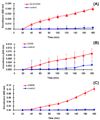
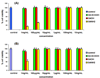
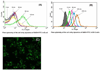
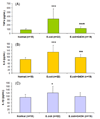
Dendrimers have emerged as topical microbicides to treat vaginal infections. This study explores the in vitro, in vivo antimicrobial activity of PAMAM dendrimers, and the associated mechanism. Interestingly, topical cervical application of 500 microg of generation-4 neutral dendrimer (G(4)-PAMAM-OH) showed potential to treat the Escherichia coli induced ascending uterine infection in guinea pig model of chorioamnionitis. Amniotic fluid collected from different gestational sacs of infected guinea pigs posttreatment showed absence of E. coli growth in the cultures plated with it. The cytokine level [tumor necrosis factor (TNFalpha) and interleukin (IL-6 and IL-1beta)] in placenta of the G(4)-PAMAM-OH treated animals were comparable to those in healthy animals while these were notably high in infected animals. Since, antibacterial activity of amine-terminated PAMAM dendrimers is known, the activity of hydroxyl and carboxylic acid terminated PAMAM dendrimers was compared with it. Though the G(4)-PAMAM-NH(2) shows superior antibacterial activity, it was found to be cytotoxic to human cervical epithelial cell line above 10 microg/mL, while the G(4)-PAMAM-OH was non-cytotoxic up to 1mg/mL concentration. Cell integrity, outer (OM) and inner (IM) membrane permeabilization assays showed that G(4)-PAMAM-OH dendrimer efficiently changed the OM permeability, while G(4)-PAMAM-NH(2) and G(3.5)-PAMAM-COOH damaged both OM and IM causing the bacterial lysis. The possible antibacterial mechanism are G(4)-PAMAM-NH(2) acts as polycation binding to the polyanionic lipopolysaccharide in E. coli, the G(4)-PAMAM-OH forms hydrogen bonds with the hydrophilic O-antigens in E. coli membrane and the G(3.5)-PAMAM-COOH acts as a polyanion, chelating the divalent ions in outer cell membrane of E. coli. This is the first study which shows that G(4)-PAMAM-OH dendrimer acts as an antibacterial agent.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial efficacy and mechanism of action of poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers against opportunistic pathogens.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019 Apr;53(4):500-507. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.12.012. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019. PMID: 30599243
-
Antibacterial action mode of quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/poly(amidoamine) dendrimer core-shell nanoparticles against Escherichia coli correlated with molecular chain conformation.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Mar;48:220-7. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.11.066. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 25579917
-
Amino-terminated generation 2 poly(amidoamine) dendrimer as a potential broad-spectrum, nonresistance-inducing antibacterial agent.AAPS J. 2013 Jan;15(1):132-42. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9416-8. Epub 2012 Nov 8. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23135925 Free PMC article.
-
PAMAM dendrimer - cell membrane interactions.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2018 Jul;257:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2018.06.005. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2018. PMID: 30008347 Review.
-
Amphiphilic dendrimers against antibiotic resistance: light at the end of the tunnel?Biomater Sci. 2023 May 16;11(10):3379-3393. doi: 10.1039/d2bm01878k. Biomater Sci. 2023. PMID: 36866708 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane perturbation action mode and structure-activity relationships of Protonectin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from the venom of the neotropical social wasp Agelaia pallipes pallipes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Oct;57(10):4632-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02311-12. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23836163 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Nitric Oxide Donors and Delivery for Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Applications.Molecules. 2022 Jan 20;27(3):674. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030674. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Polymer-Based Hydrogels for the Intravaginal Therapies-Engineering Considerations.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 2;13(9):1393. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091393. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel antimicrobial peptide dendrimers with amphiphilic surface and their interactions with phospholipids--insights from mass spectrometry.Molecules. 2013 Jun 18;18(6):7120-44. doi: 10.3390/molecules18067120. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23778121 Free PMC article.
-
Aza-Michael promoted glycoconjugation of PETIM dendrimers and selectivity in mycobacterial growth inhibitions.RSC Adv. 2023 Feb 3;13(7):4669-4677. doi: 10.1039/d2ra08196b. eCollection 2023 Jan 31. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36760308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslama SNS, Kokubun T, Halla DR. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of cicerfuran and related 2-arylbenzofurans and stilbenes. Microbiol Res. 2009;164:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Balogh LSDR, Tomalia DA, Hagnauer GL, McManus AT. Dendrimer-Silver Complexes and Nanocomposites as Antimicrobial Agents. Nano Lett. 2001;1:18–21.
-
- Benz R. Strcture and fuction of porins from gram negative bacteria. Microbial. 1988;42:359–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

