Resistance exercise volume affects myofibrillar protein synthesis and anabolic signalling molecule phosphorylation in young men
- PMID: 20581041
- PMCID: PMC2956949
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.192856
Resistance exercise volume affects myofibrillar protein synthesis and anabolic signalling molecule phosphorylation in young men
Abstract
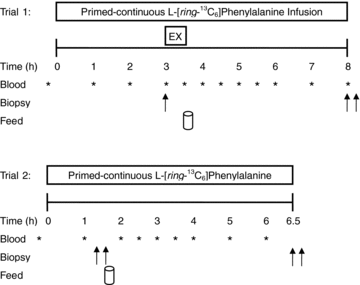
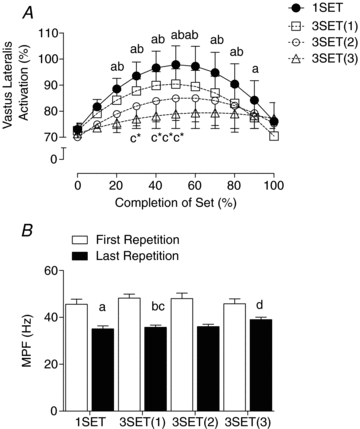
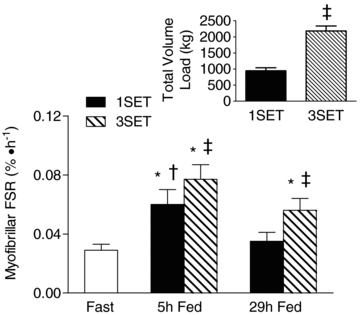
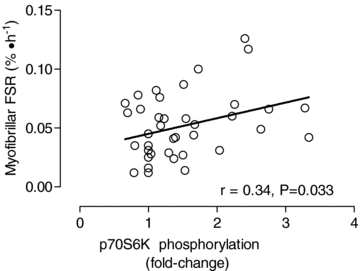
We aimed to determine if any mechanistic differences exist between a single set (1SET) and multiple sets (i.e. 3 sets; 3SET) of resistance exercise by utilizing a primed constant infusion of [ring-13C6]phenylalanine to determine myofibrillar protein synthesis (MPS) and Western blot analysis to examine anabolic signalling molecule phosphorylation following an acute bout of resistance exercise. Eight resistance-trained men (24+/-5 years, BMI=25+/-4 kg m2) were randomly assigned to perform unilateral leg extension exercise at 70% concentric one repetition maximum (1RM) until volitional fatigue for 1SET or 3SET. Biopsies from the vastus lateralis were taken in the fasted state (Fast) and fed state (Fed; 20 g of whey protein isolate) at rest, 5 h Fed, 24 h Fast and 29 h Fed post-exercise. Fed-state MPS was transiently elevated above rest at 5 h for 1SET (2.3-fold) and returned to resting levels by 29 h post-exercise. However, the exercise induced increase in MPS following 3SET was superior in amplitude and duration as compared to 1SET at both 5 h (3.1-fold above rest) and 29 h post-exercise (2.3-fold above rest). Phosphorylation of 70 kDa S6 protein kinase (p70S6K) demonstrated a coordinated increase with MPS at 5 h and 29 h post-exercise such that the extent of p70S6K phosphorylation was related to the MPS response (r=0.338, P=0.033). Phosphorylation of 90 kDa ribosomal S6 protein kinase (p90RSK) and ribosomal protein S6 (rps6) was similar for 1SET and 3SET at 24 h Fast and 29 h Fed, respectively. However, 3SET induced a greater activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B) and rpS6 at 5 h Fed. These data suggest that 3SET of resistance exercise is more anabolic than 1SET and may lead to greater increases in myofibrillar protein accretion over time.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance exercise decreases eIF2Bepsilon phosphorylation and potentiates the feeding-induced stimulation of p70S6K1 and rpS6 in young men.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):R604-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00097.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18565837
-
Short inter-set rest blunts resistance exercise-induced increases in myofibrillar protein synthesis and intracellular signalling in young males.Exp Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;101(7):866-82. doi: 10.1113/EP085647. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27126459
-
Age-related differences in the dose-response relationship of muscle protein synthesis to resistance exercise in young and old men.J Physiol. 2009 Jan 15;587(1):211-7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.164483. Epub 2008 Nov 10. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19001042 Free PMC article.
-
Fish oil supplementation suppresses resistance exercise and feeding-induced increases in anabolic signaling without affecting myofibrillar protein synthesis in young men.Physiol Rep. 2016 Mar;4(6):e12715. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12715. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27009278 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise.J Physiol. 2012 Mar 1;590(5):1049-57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.225003. Epub 2012 Jan 30. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22289911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myofibrillar protein synthesis following ingestion of soy protein isolate at rest and after resistance exercise in elderly men.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012 Jun 14;9(1):57. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-9-57. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22698458 Free PMC article.
-
Equal-Volume Strength Training With Different Training Frequencies Induces Similar Muscle Hypertrophy and Strength Improvement in Trained Participants.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 5;12:789403. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.789403. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35069251 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Changing the Contraction Mode During Resistance Training on mTORC1 Signaling and Muscle Protein Synthesis.Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 18;10:406. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00406. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31057416 Free PMC article.
-
Progression and perceptual responses to blood flow restriction resistance training among people with multiple sclerosis.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025 Jan;125(1):103-116. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05584-2. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39162881 Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of a resistance-exercise-specific signalling pathway that drives skeletal muscle growth.Nat Metab. 2025 Jul;7(7):1404-1423. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01298-7. Epub 2025 May 15. Nat Metab. 2025. PMID: 40374925
References
-
- Babault N, Pousson M, Ballay Y, Van Hoecke J. Activation of human quadriceps femoris during isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91:2628–2634. - PubMed
-
- Brody LR, Pollock MT, Roy SH, De Luca CJ, Celli B. pH-induced effects on median frequency and conduction velocity of the myoelectric signal. J Appl Physiol. 1991;71:1878–1885. - PubMed
-
- Burd NA, Tang JE, Moore DR, Phillips SM. Exercise training and protein metabolism: influences of contraction, protein intake, and sex-based differences. J Appl Physiol. 2009;106:1692–1701. - PubMed
-
- Camera DM, Edge J, Short MJ, Hawley JA, Coffey VG. Early time-course of Akt phosphorylation following endurance and resistance exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 (in press) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

