A brief nap is beneficial for human route-learning: The role of navigation experience and EEG spectral power
- PMID: 20581255
- PMCID: PMC2904102
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1828310
A brief nap is beneficial for human route-learning: The role of navigation experience and EEG spectral power
Abstract
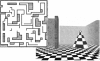
Here, we examined the effect of a daytime nap on changes in virtual maze performance across a single day. Participants either took a short nap or remained awake following training on a virtual maze task. Post-training sleep provided a clear performance benefit at later retest, but only for those participants with prior experience navigating in a three-dimensional (3D) environment. Performance improvements in experienced players were correlated with delta-rich stage 2 sleep. Complementing observations that learning-related brain activity is reiterated during post-navigation NREM sleep in rodents, the present data demonstrate that NREM sleep confers a performance advantage for spatial memory in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancement of declarative memory performance following a daytime nap is contingent on strength of initial task acquisition.Sleep. 2008 Feb;31(2):197-203. doi: 10.1093/sleep/31.2.197. Sleep. 2008. PMID: 18274266 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal slow EEG frequencies during NREM sleep are involved in spatial memory consolidation in humans.Hippocampus. 2014 Oct;24(10):1157-68. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22299. Epub 2014 May 13. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 24796545
-
Dreaming of a learning task is associated with enhanced sleep-dependent memory consolidation.Curr Biol. 2010 May 11;20(9):850-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.027. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20417102 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual navigation for memory rehabilitation in a traumatic brain injured patient.Neurocase. 2012;18(2):123-31. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2011.568499. Neurocase. 2012. PMID: 22352998
-
Reactivation, replay, and preplay: how it might all fit together.Neural Plast. 2011;2011:203462. doi: 10.1155/2011/203462. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Neural Plast. 2011. PMID: 21918724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of an automated wireless system for sleep monitoring during daytime naps.Behav Sleep Med. 2015;13(2):157-68. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2013.845782. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Behav Sleep Med. 2015. PMID: 24564261 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive neuroscience of sleep.Prog Brain Res. 2010;185:1-19. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53702-7.00001-4. Prog Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 21075230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep facilitates spatial memory but not navigation using the Minecraft Memory and Navigation task.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 25;119(43):e2202394119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202394119. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36252023 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep bolsters schematically incongruent memories.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 24;17(6):e0269439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269439. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35749391 Free PMC article.
-
Consolidation of novel word learning in native English-speaking adults.Memory. 2016;24(4):471-81. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2015.1019889. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Memory. 2016. PMID: 25768336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astur RS, St Germain SA, Baker EK, Calhoun V, Pearlson GD, Constable RT 2005. fMRI hippocampal activity during a virtual radial arm maze. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 30: 307–317 - PubMed
-
- Backhaus J, Junghanns K 2006. Daytime naps improve procedural motor memory. Sleep Med 7: 508–512 - PubMed
-
- Clemens Z, Fabo D, Halasz P 2005. Overnight verbal memory retention correlates with the number of sleep spindles. Neuroscience 132: 529–535 - PubMed
-
- Clemens Z, Fabo D, Halasz P 2006. Twenty-four hours retention of visuospatial memory correlates with the number of parietal sleep spindles. Neurosci Lett 403: 52–56 - PubMed
-
- Daurat A, Foret J, Bret-Dibat JL, Fureix C, Tiberge M 2008. Spatial and temporal memories are affected by sleep fragmentation in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 30: 91–101 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
