A phase I dose-escalation study of edotecarin (J-107088) combined with infusional 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors
- PMID: 20581657
- PMCID: PMC2931818
- DOI: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32833cb658
A phase I dose-escalation study of edotecarin (J-107088) combined with infusional 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors
Abstract
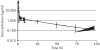
Edotecarin (J-107088), a novel inhibitor of topoisomerase I has an additive effect on colon cell lines (HCT-116) when combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). We conducted a phase I study to determine the maximum tolerated dose and recommended a phase II dose of edotecarin in combination with infusional 5-FU/leucovorin (LV) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Patients and cohorts of three to six patients were sequentially enrolled at progressively higher dose levels of edotecarin administered as a 1-h intravenous (IV) infusion every 2 weeks. The edotecarin starting dose was 6 mg/m, followed by 200 mg/m LV IV infusion administered over 2 h, then 400 mg/m bolus dose of 5-FU before the start of 2400 mg/m 5-FU continuous infusion for a further 46 h. Patients were evaluated for safety, pharmacokinetics, and tumor response according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors criteria. Fourteen patients (10 male; four female) received a total of 90 cycles (range 3-18). Dose-limiting toxicities were observed in five of the 14 patients treated in the study. All dose-limiting toxicities were related to neutropenia. Only the 6 and 8 mg/m edotecarin dose levels were explored; however, no maximum tolerated dose was declared. One confirmed complete response in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma and seven stable disease responses were achieved in the 14 treated patients. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed that edotecarin achieved and maintained apparent steady-state plasma concentrations during the IV administration in both the cycles. The administration of edotecarin in combination with infusional 5-FU/LV once every 14 days, even without the 5-FU bolus, did not permit adequate time for recovery from neutropenia.
Figures

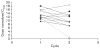

Similar articles
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of edotecarin, a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor, administered once every 3 weeks in patients with solid tumors.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;58(2):173-82. doi: 10.1007/s00280-005-0149-6. Epub 2005 Nov 25. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16308697 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of edotecarin (J-107088), a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007 Jan;59(1):139-47. doi: 10.1007/s00280-006-0267-9. Epub 2006 Jul 4. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 16819636 Clinical Trial.
-
First-in-human phase I study of infusional and bolus schedules of Deflexifol, a novel 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin formulation, after failure of standard treatment.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jun;15(3):151-157. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13144. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30843362 Clinical Trial.
-
Weekly high-dose infusional 5-fluorouracil (HD-5-FU) combinations in the treatment of advanced breast cancer: results of phase I/II studies with weekly 24-hour infusion of HD-5-FU plus high-dose folinic acid (FA) alone and in combination with paclitaxel and cisplatin.J Infus Chemother. 1996 Summer;6(3):127-32. J Infus Chemother. 1996. PMID: 9229323 Review.
-
Docetaxel in combination with fluorouracil for advanced solid tumors.Oncology (Williston Park). 1997 Aug;11(8 Suppl 8):50-2. Oncology (Williston Park). 1997. PMID: 9364544 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomics and Proteomics Characterizing the Anticancer Mechanisms of Natural Rebeccamycin Analog Loonamycin in Breast Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2022 Oct 17;27(20):6958. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206958. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296549 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol-, diol-, and carbohydrate-substituted indenoisoquinolines as topoisomerase I inhibitors: investigating the relationships involving stereochemistry, hydrogen bonding, and biological activity.J Med Chem. 2011 Jul 28;54(14):4937-53. doi: 10.1021/jm101338z. Epub 2011 Jun 28. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21710981 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Chromatographic Bioanalytical Assays for the Quantitative Determination of Marine-Derived Drugs for Cancer Treatment.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jul 23;16(7):246. doi: 10.3390/md16070246. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30041477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saif MW, Diasio RB. Edotecarin: a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2005;5:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Ciomei M, Croci V, Ciavolella A, Ballinari D, Pesenti E. Antitumor efficacy of edotecarin as a single agent and in combination with chemotherapy agents in a xenograft model. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:2856–2861. - PubMed
-
- Ciomei M, Croci V, Pesenti E, Kodera T, Monden Y, Ciavolella A, et al. Antitumor efficacy of edotecarin in combination with other cytotoxic drugs. Proc Amer Assoc Cancer Res. 2004:45. Abstract # 2099.
-
- Cavazos CM, Keir ST, Yoshinari T, Bigner DD, Friedman HS. Therapeutic activity of the topoisomerase I inhibitor J-107088 [6–N-(1-hydroxymethyla-2-hydroxyl) ethylamino-12,13-dihydro-13-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-5Hindolo( 2,3-a)-pyrrolo(3,4-c)-carbazole-5,7(6H)-dione] against pediatric and adult central nervous system tumor xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2001;48:250–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

