Weekly cyclodextrin administration normalizes cholesterol metabolism in nearly every organ of the Niemann-Pick type C1 mouse and markedly prolongs life
- PMID: 20581737
- PMCID: PMC3065173
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181ee4dd2
Weekly cyclodextrin administration normalizes cholesterol metabolism in nearly every organ of the Niemann-Pick type C1 mouse and markedly prolongs life
Abstract
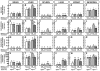
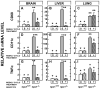
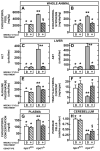
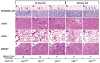
Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) disease arises from a mutation inactivating NPC1 protein that normally moves unesterified cholesterol from the late endosomal/lysosomal complex of cells to the cytosolic compartment for processing. As a result, cholesterol accumulates in every tissue of the body causing liver, lung, and CNS disease. Treatment of the murine model of this disease, the npc1 mouse, s.c. with β-cyclodextrin (4000 mg/kg) one time each week normalized cellular cholesterol metabolism in the liver and most other organs. At the same time, the hepatic dysfunction seen in the untreated npc1 mouse was prevented. The severity of cerebellar neurodegeneration also was ameliorated, although not entirely prevented, and the median lifespan of the animals was doubled. However, in contrast to these other organs, lung showed progressive macrophage infiltration with development of lipoid pneumonitis. These studies demonstrated that weekly cyclodextrin administration overcomes the lysosomal transport defect associated with the NPC1 mutation, nearly normalizes hepatic and whole animal cholesterol pools, and prevents the development of liver disease. Furthermore, this treatment slows cerebellar neurodegeneration but has little or no effect on the development of progressive pulmonary disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic administration of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin to symptomatic Npc1-deficient mice slows cholesterol sequestration in the major organs and improves liver function.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Oct;41(10):780-7. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12285. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25115571 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrin overcomes the transport defect in nearly every organ of NPC1 mice leading to excretion of sequestered cholesterol as bile acid.J Lipid Res. 2010 May;51(5):933-44. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M000257. Epub 2009 Nov 18. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19965601 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of 6-O-α-Maltosyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent Against Niemann-Pick Disease Type C.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 6;20(5):1152. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051152. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30845767 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick C disease and mobilization of lysosomal cholesterol by cyclodextrin.J Lipid Res. 2014 Aug;55(8):1609-21. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R047837. Epub 2014 Mar 24. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24664998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collaborative development of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for the treatment of Niemann-Pick type C1 disease.Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(3):330-9. doi: 10.2174/1568026613666131127160118. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24283970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Niemann-Pick disease type C: analysis of 7 patients.World J Pediatr. 2012 Feb;8(1):61-6. doi: 10.1007/s12519-011-0284-6. Epub 2011 Jun 1. World J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 21633862
-
Amino acid substitution in NPC1 that abolishes cholesterol binding reproduces phenotype of complete NPC1 deficiency in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 13;108(37):15330-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112751108. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21896731 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of 2-Hydroxypropyl-Cyclodextrins on Lipid Accumulation in Npc1-Null Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 30;21(3):898. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030898. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32019132 Free PMC article.
-
Infection by Anaplasma phagocytophilum Requires Recruitment of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol by Flotillins.mBio. 2019 Mar 26;10(2):e02783-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02783-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30914515 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic entrapment of esterified cholesterol drives continual expansion of whole body sterol pool in lysosomal acid lipase-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):G836-47. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00243.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25147230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loftus SK, Morris JA, Carstea ED, Gu JZ, Cummings C, Brown A, Ellison J, Ohno K, Rosenfeld MA, Tagle DA, Pentchev PG, Pavan WJ. Murine model of Niemann-Pick C disease: mutation in a cholesterol homeostasis gene. Science. 1997;277:232–235. - PubMed
-
- Xie C, Turley SD, Pentchev PG, Dietschy JM. Cholesterol balance and metabolism in mice with loss of function of Niemann-Pick C protein. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:E336–E344. - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Xie C, Richardson JA, Turley SD, Dietschy JM. Receptor-mediated and bulk-phase endocytosis cause macrophage and cholesterol accumulation in Niemann-Pick C disease. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:1710–1723. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Repa JJ, Valasek MA, Beltroy EP, Turley SD, German DC, Dietschy JM. Molecular, anatomical, and biochemical events associated with neurodegeneration in mice with Niemann-Pick type C disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Gondré-Lewis MC, McGlynn R, Walkley SU. Cholesterol accumulation in NPC1-deficient neurons is ganglioside dependent. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1324–1329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

