An allosteric inhibitor of substrate recognition by the SCF(Cdc4) ubiquitin ligase
- PMID: 20581844
- PMCID: PMC4445864
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1646
An allosteric inhibitor of substrate recognition by the SCF(Cdc4) ubiquitin ligase
Abstract
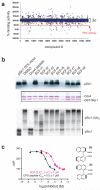
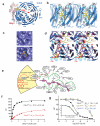
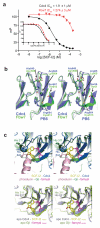
The specificity of SCF ubiquitin ligase-mediated protein degradation is determined by F-box proteins. We identified a biplanar dicarboxylic acid compound, called SCF-I2, as an inhibitor of substrate recognition by the yeast F-box protein Cdc4 using a fluorescence polarization screen to monitor the displacement of a fluorescein-labeled phosphodegron peptide. SCF-I2 inhibits the binding and ubiquitination of full-length phosphorylated substrates by SCF(Cdc4). A co-crystal structure reveals that SCF-I2 inserts itself between the beta-strands of blades 5 and 6 of the WD40 propeller domain of Cdc4 at a site that is 25 A away from the substrate binding site. Long-range transmission of SCF-I2 interactions distorts the substrate binding pocket and impedes recognition of key determinants in the Cdc4 phosphodegron. Mutation of the SCF-I2 binding site abrogates its inhibitory effect and explains specificity in the allosteric inhibition mechanism. Mammalian WD40 domain proteins may exhibit similar allosteric responsiveness and hence represent an extensive class of druggable target.
Figures
Comment in
-
Inhibitors for E3 ubiquitin ligases.Nat Biotechnol. 2010 Jul;28(7):682-4. doi: 10.1038/nbt0710-682. Nat Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20622837 No abstract available.
References
-
- Willems AR, Schwab M, Tyers M. A hitchhiker’s guide to the cullin ubiquitin ligases: SCF and its kin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1695:133–170. - PubMed
-
- Petroski MD, Deshaies RJ. Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:9–20. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Nalepa G, Rolfe M, Harper JW. Drug discovery in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:596–613. - PubMed
-
- Bai C, et al. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

