Sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary hypertension: Clinical features and outcomes in Arab patients
- PMID: 20582173
- PMCID: PMC2883203
- DOI: 10.4103/1817-1737.62471
Sarcoidosis-associated pulmonary hypertension: Clinical features and outcomes in Arab patients
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) occurs in many patients with interstitial lung disease, including sarcoidosis. We explored the frequency, clinical characteristics and outcomes of PH in Arab patients diagnosed with pulmonary sarcoidosis.
Methods: A retrospective study in three tertiary hospitals was performed on 96 patients who underwent Doppler echocardiography. Demographic and clinical characteristics, physiological studies and computed tomography (CT) results were collected, and compared between patients with and without PH.
Results: Twenty (20.8%) patients were found to have PH. Patients with PH were more likely to be symptomatic (cough, P = 0.008; dyspnea, P = 0.04), to have an advanced radiographic stage (P = 0.001), and to be receiving systemic therapy (P = 0.001), compared to those without PH. Physiological data including pulmonary function test parameters, arterial blood gas levels and oxygen saturation at rest and after exercise were all significantly lower in patients with PH compared to those without PH. Comparison of CT patterns between patients with and without PH showed significant differences in the frequencies of ground-glass opacity (61.5 vs. 28.8%, P = 0.032) and fibrosis (76.9 vs. 44.2%, P = 0.035). In total, four patients died during the study period, including three with evidence of PH.
Conclusions: The frequency of PH in the present study was 20.8%. Clinical, physiologic and radiographic characteristics appeared to differentiate patients with PH from those without PH. The presence of PH contributed to poor outcomes in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis.
Keywords: Computed tomography; echocardiography; pulmonary function test; pulmonary hypertension; sarcoidosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
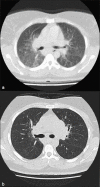
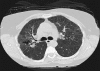


References
-
- Costabel U. Sarcoidosis: clinical update. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2001;32:56s–68. - PubMed
-
- Chaouat A, Bugnet AS, Kadaoui N, Schott R, Enache I, Ducoloné A, et al. Severe pulmonary hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:189–94. - PubMed
-
- Chang B, Wigley FM, White B, Wise RA. Scleroderma patients with combined pulmonary hypertension and interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2398–405. - PubMed
-
- Lettieri CJ, Nathan SD, Barnett SD, Ahmad S, Shorr AF. Prevalence and outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2006;129:746–52. - PubMed
-
- Shorr AF, Davies DB, Nathan SD. Predicting mortality in patients with sarcoidosis awaiting lung transplantation. Chest. 2003;124:922–8. - PubMed

