The effect of radiotherapy on NKT cells in patients with advanced head and neck cancer
- PMID: 20582589
- PMCID: PMC11030092
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0877-2
The effect of radiotherapy on NKT cells in patients with advanced head and neck cancer
Abstract
Background: Cancer immunotherapy with NKT cells is a potential new treatment strategy for advanced head and neck cancer. NKT cell therapy is promising due to its unique anti-tumor activity and higher degree of safety compared to current therapies. Radiotherapy is indispensable as a standard treatment for advanced head and neck cancer. To elucidate the possibility of using NKT cells as an adjuvant immunotherapy with radiotherapy, we examined the effect of radiotherapy on NKT cells in patients with head and neck cancer.
Methods: The number, IFN-gamma production and proliferation capacity of NKT cells were analyzed before and after 50 Gy radiation therapy in 12 patients with stage IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The cytotoxic activity of NKT cells was examined in vitro.
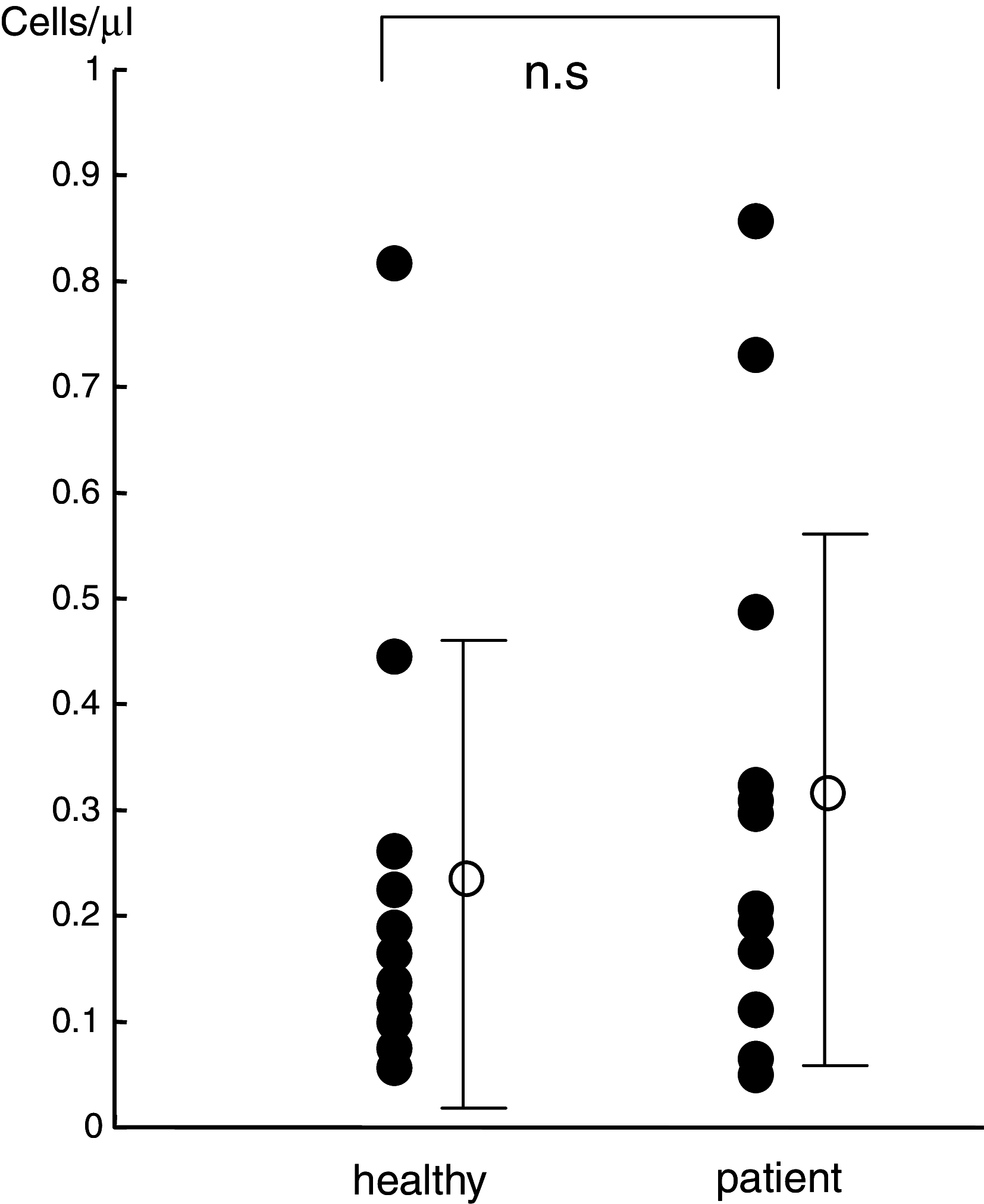
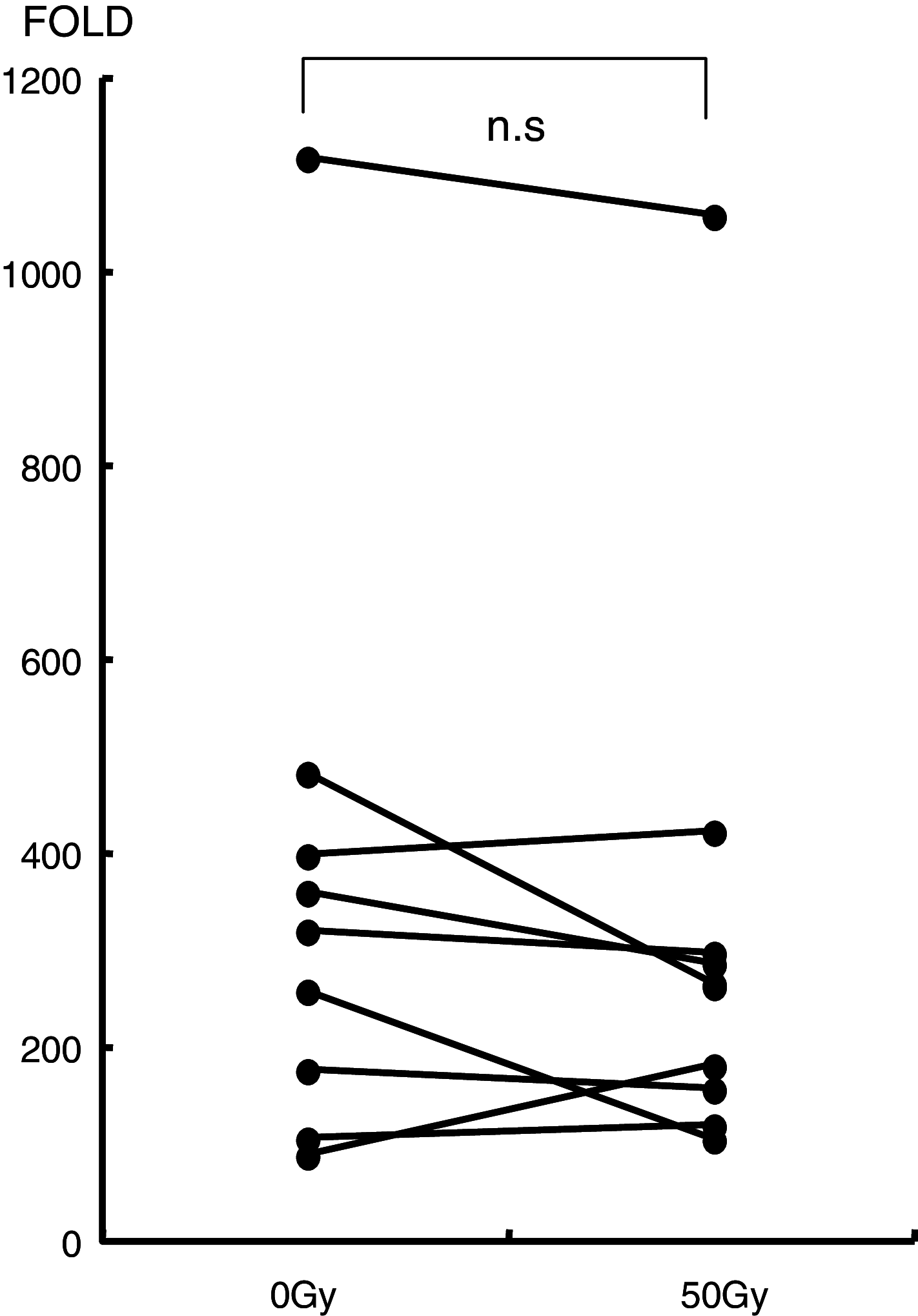
Results: The number of NKT cells in the blood varied widely between patients. After radiation therapy, the population of CD3 T cells decreased significantly, while the NKT cell population remained stable. The number of NKT cells was the same after radiation therapy as before. IFN-gamma production from NKT cells collected just after radiotherapy was impaired after stimulation with exogenous ligand, but the proliferative responses of these NKT cells was enhanced in comparison to those collected before radiation therapy. Furthermore, the proliferated NKT cells displayed a significant level of anti-tumor activity.
Conclusion: NKT cells are relatively resistant to radiation and might therefore be suitable for adjuvant immunotherapy to eradicate remnant cancer cells in patients who have undergone radiation therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck squamous cell carcinomas: II--clinical results.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Oct 1;60(2):374-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.010. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15380569 Clinical Trial.
-
[SIB-IMRT radiotherapy given concomitantly with cisplatin for locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancer (SCHNC). Evaluation of the early results and toxicity].Otolaryngol Pol. 2011 Sep;65(5 Suppl):117-25. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6657(11)70719-3. Otolaryngol Pol. 2011. PMID: 22000261 Polish.
-
Regulatory T cells induce CD4- NKT cell anergy and suppress NKT cell cytotoxic function.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Dec;68(12):1935-1947. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02417-6. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31641795 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant therapy in head and neck cancer.CA Cancer J Clin. 1998 Jul-Aug;48(4):199-209. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.48.4.199. CA Cancer J Clin. 1998. PMID: 9676534 Review.
-
Radiation-induced hypothyroidism after treatment of head and neck cancer.Dan Med J. 2016 Mar;63(3):B5213. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 26931197 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic impact of invariant natural killer T cells in solid and hematological tumors; systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Biomark. 2024;41(2):155-164. doi: 10.3233/CBM-240069. Cancer Biomark. 2024. PMID: 39302356 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Application of iNKT Cell-mediated Anti-tumor Activity Against Lung Cancer and Head and Neck Cancer.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 7;9:2021. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02021. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30245690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Natural Killer T Cells in Solid Malignancies.Cells. 2021 May 27;10(6):1329. doi: 10.3390/cells10061329. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34072042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD1d-Invariant Natural Killer T Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy: α-Galactosylceramide and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 2;9:1519. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01519. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30013569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the composition of lymphocyte subpopulations in non-relapse and relapse patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck before, during radiochemotherapy and in the follow-up period: a multicenter prospective study of the German Cancer Consortium Radiation Oncology Group (DKTK-ROG).Radiat Oncol. 2021 Jul 31;16(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01868-5. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34332614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hainsworth JD, Meluch AA, McClurkan S, Gray JR, Stroup SL, Burris HA, III, Yardley DA, Bradof JE, Yost K, Ellis JK, Greco FA. Induction paclitaxel, carboplatin, and infusional 5-FU followed by concurrent radiation therapy and weekly paclitaxel/carboplatin in the treatment of locally advanced head and neck cancer: a phase II trial of the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network. Cancer J. 2002;8:298–300. doi: 10.1097/00130404-200207000-00007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

