SAM domain-dependent activity of PfTKL3, an essential tyrosine kinase-like kinase of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 20582613
- PMCID: PMC2933843
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0434-3
SAM domain-dependent activity of PfTKL3, an essential tyrosine kinase-like kinase of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
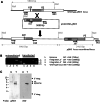
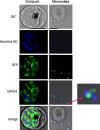
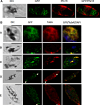
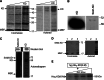
Over the last decade, several protein kinases inhibitors have reached the market for cancer chemotherapy. The kinomes of pathogens represent potentially attractive targets in infectious diseases. The functions of the majority of protein kinases of Plasmodium falciparum, the parasitic protist responsible for the most virulent form of human malaria, remain unknown. Here we present a thorough characterisation of PfTKL3 (PF13_0258), an enzyme that belongs to the tyrosine kinase-like kinase (TKL) group. We demonstrate by reverse genetics that PfTKL3 is essential for asexual parasite proliferation in human erythrocytes. PfTKL3 is expressed in both asexual and gametocytes stages, and in the latter the protein co-localises with cytoskeleton microtubules. Recombinant PfTKL3 displays in vitro autophosphorylation activity and is able to phosphorylate exogenous substrates, and both activities are dramatically dependent on the presence of an N-terminal "sterile alpha-motif" domain. This study identifies PfTKL3 as a validated drug target amenable to high-throughput screening.
Figures





References
-
- White NJ, Nosten F, Looareesuwan S, Watkins WM, Marsh K, Snow RW, Kokwaro G, Ouma J, Hien TT, Molyneux ME, Taylor TE, Newbold CI, Ruebush TK, 2nd, Danis M, Greenwood BM, Anderson RM, Olliaro P. Averting a malaria disaster. Lancet. 1999;353:1965–1967. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07367-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dondorp AM, Nosten F, Yi P, Das D, Phyo AP, Tarning J, Lwin KM, Ariey F, Hanpithakpong W, Lee SJ, Ringwald P, Silamut K, Imwong M, Chotivanich K, Lim P, Herdman T, An SS, Yeung S, Singhasivanon P, Day NP, Lindegardh N, Socheat D, White NJ. Artemisinin resistance in plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:455–467. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808859. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dondorp AM, Yeung S, White L, Nguon C, Day NP, Socheat D, von Seidlein L. Artemisinin resistance: current status and scenarios for containment. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:272–280 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

