Helical tomotherapy with concurrent capecitabine for the treatment of inoperable pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 20584299
- PMCID: PMC2903902
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-60
Helical tomotherapy with concurrent capecitabine for the treatment of inoperable pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Helical tomotherapy, an advanced intensity-modulated radiation therapy with integrated CT imaging, permits highly conformal irradiation with sparing of normal tissue. Capecitabine, a pro-drug of 5-FU that induces thymidine phosphorylase can achieve higher levels of intracellular 5-FU when administered concurrently with radiation. We evaluated the feasibility as well as the clinical outcome of concurrent administration of capecitabine with tomotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.
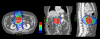
Methods: Nineteen patients with advanced pancreatic cancer including primarily unresectable disease and recurrence after curative surgery were included in the study. Two planning target volumes (PTV) were entered: PTV1 is gross tumor volume; and PTV2, the volume of the draining lymph nodes. The total doses to target 1 and target 2 were 55 and 50 Gy, respectively. Capecitabine at 1600 mg/m2/day was administered on each day of irradiation.
Results: Twenty six measurable lesions were evaluated. Overall in-field response rate was 42.3%; partial responses were achieved in 53.3% of the pancreatic masses, 28.6% of distant metastatic lesions and 25.0% of regional lymph nodes. The median duration of follow-up after tomotherapy was 6.5 months. None of the lesions showed in-field progression. Treatment was well tolerated with only minor toxicities such as grade 1 nausea (one patient), grade 1 hand-foot syndrome (one patient) and grade 1/2 fatigue (three patients).
Conclusions: Helical tomotherapy with concurrent capecitabine is a feasible option without significant toxicities in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. We achieved excellent conformal distribution of radiation doses and minimal treatment-related toxicities with promising target volume responses.
Figures
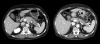
Similar articles
-
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and concurrent capecitabine for pancreatic cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Jun 1;59(2):454-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.11.019. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15145162
-
Efficacy and tolerability of limited field radiotherapy with concurrent capecitabine in locally advanced pancreatic cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2010 Sep;22(7):570-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2010. PMID: 20650619
-
Hypofractionated image-guided IMRT in advanced pancreatic cancer with simultaneous integrated boost to infiltrated vessels concomitant with capecitabine: a phase I study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Dec 1;87(5):1000-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.09.012. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 24267968 Clinical Trial.
-
Chemoradiation for ductal pancreatic carcinoma: principles of combining chemotherapy with radiation, definition of target volume and radiation dose.JOP. 2005 May 10;6(3):216-30. JOP. 2005. PMID: 15883472 Review.
-
Capecitabine: a review.Clin Ther. 2005 Jan;27(1):23-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.01.005. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 15763604 Review.
Cited by
-
Locally advanced pancreatic cancer successfully treated with high-dose helical tomotherapy.Int Cancer Conf J. 2018 Aug 13;7(4):152-155. doi: 10.1007/s13691-018-0340-3. eCollection 2018 Oct. Int Cancer Conf J. 2018. PMID: 31149536 Free PMC article.
-
Early experience of helical tomotherapy for hepatobiliary radiotherapy.Case Reports Hepatol. 2011;2011:545267. doi: 10.1155/2011/545267. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Case Reports Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 25954545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oettle H, Post S, Neuhaus P, Gellert K, Langrehr J, Ridwelski K, Schramm H, Fahlke J, Zuelke C, Burkart C, Gutberlet K, Kettner E, Schmalenberg H, Weigang-Koehler K, Bechstein W, Niedergethmann M, Schmidt-Wolf I, Roll L, Doerken B, Riess H. Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine vs observation in patients undergoing curative-intent resection of pancreatic cancer: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:267–277. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.3.267. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ben-Josef E, Shields AF, Vaishampayan U, Vaitkevicius V, El-Rayes BF, McDermott P, Burmeister J, Bossenberger T, Philip PA. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and concurrent capecitabine for pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59:454–459. - PubMed
-
- Moertel CG, Frytak S, Hahn RG, O'Connell MJ, Reitemeier RJ, Rubin J, Schutt AJ, Weiland LH, Childs DS, Holbrook MA, Lavin PT, Livstone E, Spiro H, Knowlton A, Kalser M, Barkin J, Lessner H, Mann-Kaplan R, Ramming K, Douglas HO Jr, Thomas P, Nave H, Bateman J, Lokich J, Brooks J, Chaffey J, Corson JM, Zamcheck N, Novak JW. Therapy of locally unresectable pancreatic carcinoma: a randomized comparison of high dose (6000 rads) radiation alone, moderate dose radiation (4000 rads + 5-fluorouracil), and high dose radiation + 5-fluorouracil: The Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group. Cancer. 1981;48:1705–1710. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811015)48:8<1705::AID-CNCR2820480803>3.0.CO;2-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

