Loss of GM-CSF signalling in non-haematopoietic cells increases NSAID ileal injury
- PMID: 20584783
- PMCID: PMC4296557
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2009.203893
Loss of GM-CSF signalling in non-haematopoietic cells increases NSAID ileal injury
Abstract
Background: Administration of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) relieves symptoms in Crohn's disease (CD). It has been reported that reduced GM-CSF bioactivity is associated with more aggressive ileal behaviour and that GM-CSF-null mice exhibit ileal barrier dysfunction and develop a transmural ileitis following exposure to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). STAT5 signalling is central to GM-CSF action. It was therefore hypothesised that GM-CSF signalling in non-haematopoietic cells is required for ileal homeostasis.
Methods: Bone marrow (BM) chimeras were generated by reconstituting irradiated GM-CSF receptor (gm-csfr) beta chain or GM-CSF (gm-csf) deficient mice with wild type BM (WTBM-->GMRKO and WTBM-->GMKO). Intestinal barrier function and the response to NSAID-induced ileal injury were examined. Expression of gm-csf, gm-csfr or stat5 in Caco-2 and HT-29 intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) lines was knocked down and the effect of GM-CSF signalling on IEC survival and proliferation was determined.
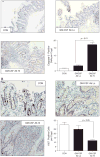
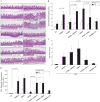
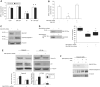
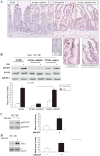
Results: Elevated levels of GM-CSF autoantibodies in ileal CD were found to be associated with dysregulation of IEC survival and proliferation. GM-CSF receptor-deficient mice and WTBM-->GMRKO chimeras exhibited ileal hyperpermeability. NSAID exposure induced a transmural ileitis in GM-CSF receptor-deficient mice and WTBM-->GMRKO chimeras. Transplantation of wild type BM into GM-CSF-deficient mice prevented NSAID ileal injury and restored ileal barrier function. Ileal crypt IEC proliferation was reduced in WTBM-->GMRKO chimeras, while STAT5 activation in ileal IEC following NSAID exposure was abrogated in WTBM-->GMRKO chimeras. Following knock down of gm-csf, gm-csfr alpha or beta chain or stat5a/b expression in Caco-2 cells, basal proliferation was suppressed. GM-CSF normalised proliferation of Caco-2 cells exposed to NSAID, which was blocked by stat5a/b RNA interference.
Conclusions: Loss of GM-CSF signalling in non-haematopoietic cells increases NSAID ileal injury; furthermore, GM-CSF signalling in non-haematopoietic cells regulates ileal epithelial homeostasis via the STAT5 pathway. The therapeutic use of GM-CSF may therefore be beneficial in chronic ileitis associated with CD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Hampe J, Franke A, Rosenstiel P, et al. A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nat Genet. 2007;39:207–11. - PubMed
-
- Drumm B, Vaughan D. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for Crohn's disease. Lancet. 2003;361:1830. author reply 1830–1. - PubMed
-
- Korzenik JR, Dieckgraefe BK, Valentine JF, et al. Sargramostim for active Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2193–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
