The codon specificity of eubacterial release factors is determined by the sequence and size of the recognition loop
- PMID: 20584893
- PMCID: PMC2905760
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2117010
The codon specificity of eubacterial release factors is determined by the sequence and size of the recognition loop
Abstract
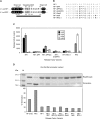
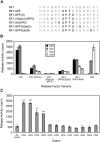
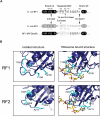
The two codon-specific eubacterial release factors (RF1: UAA/UAG and RF2: UAA/UGA) have specific tripeptide motifs (PXT/SPF) within an exposed recognition loop shown in recent structures to interact with stop codons during protein synthesis termination. The motifs have been inferred to be critical for codon specificity, but this study shows that they are insufficient to determine specificity alone. Swapping the motifs or the entire loop between factors resulted in a loss of codon recognition rather than a switch of codon specificity. From a study of chimeric eubacterial RF1/RF2 recognition loops and an atypical shorter variant in Caenorhabditis elegans mitochondrial RF1 that lacks the classical tripeptide motif PXT, key determinants throughout the whole loop have been defined. It reveals that more than one configuration of the recognition loop based on specific sequence and size can achieve the same desired codon specificity. This study has provided unexpected insight into why a combination of the two factors is necessary in eubacteria to exclude recognition of UGG as stop.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coevolution between Stop Codon Usage and Release Factors in Bacterial Species.Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Sep;33(9):2357-67. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw107. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27297468 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of stop-codon reading on the ribosome.Nature. 2010 Jun 17;465(7300):947-50. doi: 10.1038/nature09082. Epub 2010 May 30. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20512119
-
R213I mutation in release factor 2 (RF2) is one step forward for engineering an omnipotent release factor in bacteria Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 8;292(36):15134-15142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.785238. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28743745 Free PMC article.
-
A tripeptide discriminator for stop codon recognition.FEBS Lett. 2002 Mar 6;514(1):30-3. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02330-x. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11904176 Review.
-
Molecular recognition and catalysis in translation termination complexes.Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 May;36(5):282-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.02.001. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011. PMID: 21420300 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution and diversification of the organellar release factor family.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Nov;29(11):3497-512. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss157. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22688947 Free PMC article.
-
Structural aspects of translation termination on the ribosome.RNA. 2011 Aug;17(8):1409-21. doi: 10.1261/rna.2733411. Epub 2011 Jun 23. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21700725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering a genomically recoded organism with one stop codon.Nature. 2025 Mar;639(8054):512-521. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08501-x. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39910296 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic mutagenesis of stop codon nucleotides reveals the chemical prerequisites for release factor-mediated peptide release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 16;115(3):E382-E389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714554115. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29298914 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of release factor eRF1-1 from Arabidopsis thaliana.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013 Nov;69(Pt 11):1295-8. doi: 10.1107/S1744309113027784. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2013. PMID: 24192373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Askarian-Amiri ME, Pel HJ, Guevremont D, McCaughan KK, Poole ES, Sumpter VG, Tate WP 2000. Functional characterization of yeast mitochondrial release factor 1. J Biol Chem 275: 17241–17248 - PubMed
-
- Bjornsson A, Mottagui-Tabar S, Isaksson LA 1998. The analysis of translational activity using a reporter gene constructed from repeats of an antibody-binding domain from protein A. Methods Mol Biol 77: 75–91 - PubMed
-
- Coulondre C, Miller JH 1977. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. III. Additional correlation of mutational sites with specific amino acid residues. J Mol Biol 117: 525–567 - PubMed
-
- Crick FH 1958. On protein synthesis. Symp Soc Exp Biol 12: 138–163 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
