Isoform-specific prolongation of Kv7 (KCNQ) potassium channel opening mediated by new molecular determinants for drug-channel interactions
- PMID: 20584905
- PMCID: PMC2934696
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116392
Isoform-specific prolongation of Kv7 (KCNQ) potassium channel opening mediated by new molecular determinants for drug-channel interactions
Abstract
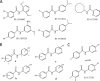
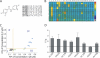
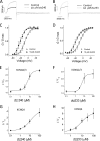
Kv7 channels, especially Kv7.2 (KCNQ2) and Kv7.3 (KCNQ3), are key determinants for membrane excitability in the brain. Some chemical modulators of KCNQ channels are in development for use as anti-epileptic drugs, such as retigabine (D-23129, N-(2-amino-4-(4-fluorobenzylamino)-phenyl)), which was recently approved for clinical use. In addition, several other compounds were also reported to potentiate activity of the Kv7 channels. It is therefore of interest to investigate compound-channel interactions, so that more insights may be gained to aid future development of therapeutics. We have conducted a screen of 20,000 compounds for KCNQ2 potentiators using rubidium flux combined with atomic absorption spectrometry. Here, we report the characterization of a series of new structures that display isoform specificity and induce a marked reduction of deactivation distinct from that of retigabine. Furthermore, KCNQ2(W236L), a previously reported mutation that abolishes sensitivity to retigabine, remains fully sensitive to these compounds. This result, together with mutagenesis and other studies, suggests that the reported compounds confer a unique mode of action and involve new molecular determinants on the channel protein, consistent with the idea of recognizing a new site on channel protein.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Sequence determinants of subtype-specific actions of KCNQ channel openers.J Physiol. 2017 Feb 1;595(3):663-676. doi: 10.1113/JP272762. Epub 2016 Sep 23. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27506413 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of M-type KCNQ (Kv7) K+ channel assembly.J Neurosci. 2006 Apr 5;26(14):3757-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5017-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16597729 Free PMC article.
-
The KCNQ2/3 selective channel opener ICA-27243 binds to a novel voltage-sensor domain site.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Nov 13;465(2):138-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.08.071. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19733209
-
The therapeutic potential of neuronal KCNQ channel modulators.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003 Dec;7(6):737-48. doi: 10.1517/14728222.7.6.737. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003. PMID: 14640909 Review.
-
Identifying the mechanism of action of the Kv7 channel opener, retigabine in the treatment of epilepsy.Neurol Sci. 2023 Nov;44(11):3819-3825. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06955-x. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37442907 Review.
Cited by
-
The gating charge pathway of an epilepsy-associated potassium channel accommodates chemical ligands.Cell Res. 2013 Sep;23(9):1106-18. doi: 10.1038/cr.2013.82. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23797855 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic basis for therapeutic activation of neuronal potassium channels.Nat Commun. 2015 Sep 3;6:8116. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9116. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26333338 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of vascular smooth muscle Kv7.4, Kv7.5, and Kv7.4/7.5 channels by ML213 and ICA-069673.Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;86(3):330-41. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.093799. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24944189 Free PMC article.
-
Potassium channels in peripheral pain pathways: expression, function and therapeutic potential.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013 Dec;11(6):621-40. doi: 10.2174/1570159X113119990042. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24396338 Free PMC article.
-
Four drug-sensitive subunits are required for maximal effect of a voltage sensor-targeted KCNQ opener.J Gen Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;150(10):1432-1443. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201812014. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Gen Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30166313 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

